Page 124 - Packed bed columns for absorption, desorption, rectification and direct heat transfer
P. 124
119
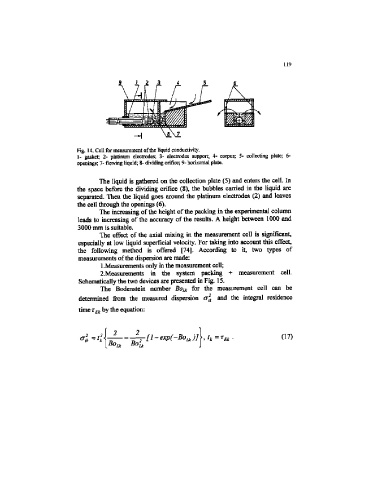
Fig. 14. Cell for measurement of the liquid conductivity.
1- gasket; 2- platinum electrodes; 3- electrodes support; 4- eoipus; 5- collecting plate; 6-
openings; 7- flowing liquid; 8- dividing orifice; 9- horizontal plate.
The liquid is gathered on the collection plate (5) and enters the cell. In
the space before the dividing orifice (8), the bubbles carried in the liquid are
separated. Then the liquid goes around the platinum electrodes (2) and leaves
the cell through the openings (6).
The increasing of the height of the packing in the experimental column
leads to increasing of the accuracy of the results. A height between 1000 and
3000 mm is suitable.
The effect of the axial mixing in the measurement cell is significant,
especially at low liquid superficial velocity. For taking into account this effect,
the following method is offered [74]. According to it, two types of
measurements of the dispersion are made:
1 .Measurements only in the measurement cell;
2.Measurements in the system packing + measurement cell.
Schematically the two devices are presented in Fig. 15.
The Bodenstein number Boa for the measurement cell can be
determined from the measured dispersion <jf k and the integral residence
time T Ek by the equation;
(17)
-[l-exp(-Bo Uc)]\>h=T i Ek
Bo
Bo Uc Ik