Page 103 - Partition & Adsorption of Organic Contaminants in Environmental Systems
P. 103
ap eq
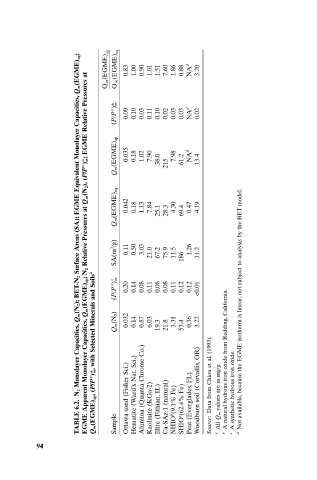
Q m(EGME) eq; EGME Relative Pressures at EGME) Q m ( (P/P°)* EGME) Q m ( m 0.83 0.09 1.00 0.10 0.90 0.03 1.01 0.11 1.51 0.10 7.60 0.02 1.86 0.03 0.88 0.03 NA d NA d 3.20 0.02
EGME Equivalent Monolayer Capacities, (P/P°)°; m Q m(EGME) ap 0.035 0.18 1.02 7.90 38.0 215 7.98 61.2 NA d 13.4
Surface Areas (SA); Relative Pressures at Q m(N 2), Q m(EGME) eq SA(m 2 /g) 0.042 0.11 0.18 0.50 1.13 3.03 7.84 21.0 25.1 67.2 28.3 75.9 4.30 11.5 69.4 186 0.47 1.26 4.19 11.2
BET-N 2 Q m(EGME) ap;N 2 (P/P°)° m 0.20 0.14 0.08 0.11 0.06 0.08 0.11 0.12 0.12 <0.01
Q m(N 2); with Selected Minerals and Soils a Q m(N 2) 0.032 0.14 0.87 6.03 19.3 21.8 3.31 53.4 0.36 3.22 Not available, because the EGME isotherm is linear, not subject to analysis by the BET model.
Monolayer Capacities, m Sci.) OR) (1993). A natural hydrous iron oxide from Redding, California.
N 2 EGME Apparent Monolayer Capacities, Ottawa sand (Fisher Sci.) Alumina (Quanta Chrome Co.) IL) FL) Woodburn soil (Corvallis, Data from Chiou et al. values are in mg/g. A synthetic hydrous iron oxide.
6.2. Q m(EGME) ap,(P/P°)*, Hematite (Ward’s Nat. Kaolinite (KGa-2) Ca-SAz-1 (natural) NHIO b (9.1% Fe) SHIO c (62.4% Fe) Peat (Everglades,
TABLE Sample Illite (Fithian, Source: a All Q m b c d
94