Page 59 -
P. 59
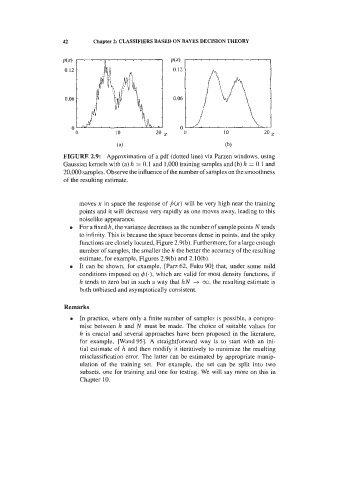
2.5 Feature Assessment 45
Group 3 1 3 5 0 6198.5
Figure 2.21. Kruskal-Wallis test for feature ART of the cork stoppers data.
It is also useful, as we have seen in previous sections, to compute the
correlations among the features in order to eventually discard features that are
highly correlated with other ones. Figure 2.22 shows the correlation matrix for the
cork stoppers features. All of them are significantly correlated. For instance, the
total perimeter of the defects (PRT), not surprisingly, has a high correlation (0.98)
with their total area (ART). The same happens for the big defects with a 0.99
correlation for the respective features (PRTG and ARTG). It is therefore
reasonable to discard one of the PRT, ART features when the other one is used,
and likewise for the PRTG, ARTG features.
Figure 2.22. Correlation matrix for the cork stoppers features. All correlations are
significant at p=0.05 level.
Once all the inference tests have been performed it is convenient to summarize
the results in a sorted table, as was done in Table 2.1 for the Kruskal- Wallis test
results for all features. Sorting should be done for the p values and in case of ties