Page 98 - Performance Leadership
P. 98
Chapter 6 One Version of the Truth • 87
Case Study 2: European Railway Company
The key term in the railway business is train, and many different defini-
tions exist. High regulation adds to complexity and many stakeholders
have a role to play. Typically, a train company has a government license
to operate a train schedule. The rail infrastructure is often managed by
a separate organization. Perhaps one or both are government owned or
privately held. A reason to split the train operator and infrastructure com-
pany is to increase competition and create more efficiency, with multi-
ple suppliers using the same infrastructure. The same can be seen in, for
instance, telecom and the utilities industries. Each stakeholder, internal
or external, will have a slightly different view of the core business. Let’s
explore a number of different views of what constitutes a train using the
example of a major European country railway system (see Table 6.3).
For passengers, a train consists of a set of carriages, pulled by a loco-
motive. This “train” takes passengers from one train station to another.
One might think this definition equates “train” with a journey. How-
ever, a train passenger may have to “change trains,” and thus take mul-
tiple trains to get to a particular final destination. Already differences
in term definitions emerge; that is, this isn’t the same information that
is held on the train ticket. So, for every 1,000 completed journeys the
rail operator sells, travelers may utilize 2,500 trains.
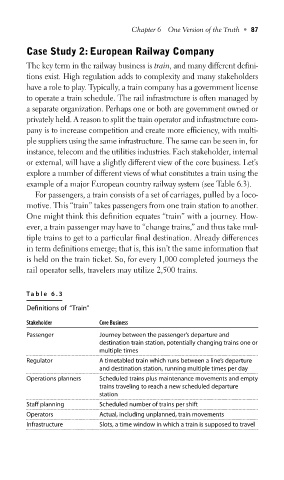
Table 6.3
Definitions of “Train”
Stakeholder Core Business
Passenger Journey between the passenger’s departure and
destination train station, potentially changing trains one or
multiple times
Regulator A timetabled train which runs between a line’s departure
and destination station, running multiple times per day
Operations planners Scheduled trains plus maintenance movements and empty
trains traveling to reach a new scheduled departure
station
Staff planning Scheduled number of trains per shift
Operators Actual, including unplanned, train movements
Infrastructure Slots, a time window in which a train is supposed to travel