Page 243 - Petroleum and Gas Field Processing
P. 243
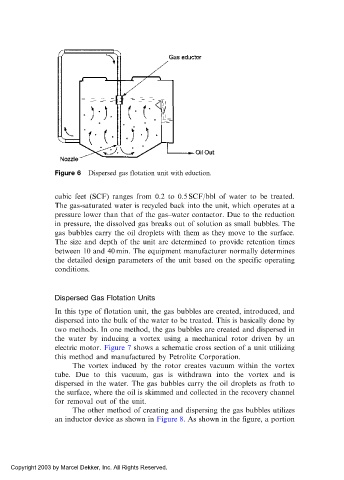
Figure 6 Dispersed gas flotation unit with eduction.
cubic feet (SCF) ranges from 0.2 to 0.5 SCF/bbl of water to be treated.
The gas-saturated water is recycled back into the unit, which operates at a
pressure lower than that of the gas–water contactor. Due to the reduction
in pressure, the dissolved gas breaks out of solution as small bubbles. The
gas bubbles carry the oil droplets with them as they move to the surface.
The size and depth of the unit are determined to provide retention times
between 10 and 40 min. The equipment manufacturer normally determines
the detailed design parameters of the unit based on the specific operating
conditions.
Dispersed Gas Flotation Units
In this type of flotation unit, the gas bubbles are created, introduced, and
dispersed into the bulk of the water to be treated. This is basically done by
two methods. In one method, the gas bubbles are created and dispersed in
the water by inducing a vortex using a mechanical rotor driven by an
electric motor. Figure 7 shows a schematic cross section of a unit utilizing
this method and manufactured by Petrolite Corporation.
The vortex induced by the rotor creates vacuum within the vortex
tube. Due to this vacuum, gas is withdrawn into the vortex and is
dispersed in the water. The gas bubbles carry the oil droplets as froth to
the surface, where the oil is skimmed and collected in the recovery channel
for removal out of the unit.
The other method of creating and dispersing the gas bubbles utilizes
an inductor device as shown in Figure 8. As shown in the figure, a portion
Copyright 2003 by Marcel Dekker, Inc. All Rights Reserved.