Page 221 - Petrophysics 2E
P. 221
194 PETROPHYSICS: RESERVOIR ROCK PROPERTIES
b. Give an explanation for the deviation of the data that occurs for
the high-permeability core.
c. Match your data to Figure 3.13 and use it to identify the most likely
rock type of the reservoir.
d. Determine the correct mean value of the permeability.
5. If a core has a porosity of 18% and an irreducible water saturation of
24%, what is the permeability of the sample?
6. What is the matrix permeability of the core described in Problem 5 if
the effective pore throat radius is 3.5 prn and the cementation factor
is 2? Estimate the tortuosity of the sample.
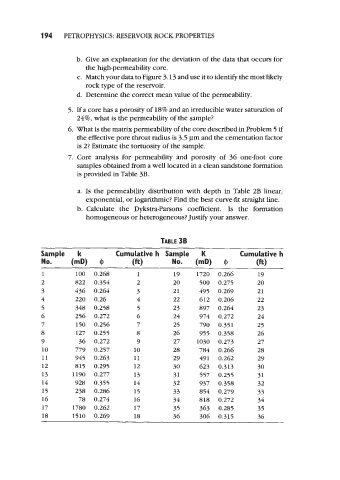
7. Core analysis for permeability and porosity of 36 one-foot core
samples obtained from a well located in a clean sandstone formation
is provided in Table 3B.
a. Is the permeability distribution with depth in Table 2B linear,
exponential, or logarithmic? Find the best curve-fit straight line.
b. Calculate the Dykstra-Parsons coefficient. Is the formation
homogeneous or heterogeneous? Justify your answer.
TABLE 38
Sample k Cumulative h Sample K Cumulative h
No. (mD) 9 (W No. (mD) 9 (fit)
1 loo 0.268 1 19 1720 0.266 19
2 822 0.354 2 20 500 0.275 20
3 436 0.264 3 21 495 0.269 21
4 220 0.26 4 22 612 0.206 22
5 348 0.258 5 23 897 0.264 23
6 256 0.272 6 24 974 0.272 24
7 150 0.256 7 25 790 0.351 25
8 127 0.255 8 26 955 0.358 26
9 36 0.272 9 27 1030 0.273 27
10 779 0.257 10 28 784 0.266 28
11 945 0.263 11 29 491 0.262 29
12 815 0.295 12 30 623 0.313 30
13 1190 0.277 13 31 557 0.255 31
14 928 0.355 14 32 937 0.358 32
15 238 0.286 15 33 854 0.279 33
16 78 0.274 16 34 818 0.272 34
17 1780 0.262 17 35 363 0.285 35
18 1510 0.269 18 36 306 0.315 36