Page 193 - Petrophysics
P. 193
166 PETROPHYSICS: RESERVOIR ROCK PROPERTIES
E x
d
0
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 'IJI
Vtriation, V
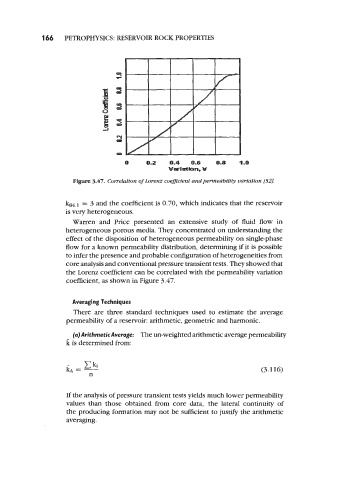
Figure 3.47. Correlation of Lorenz coeflcient andpemzeabtliv vartatton [52].
k84,* = 3 and the coefficient is 0.70, which indicates that the reservoir
is very heterogeneous.
Warren and Price presented an extensive study of fluid flow in
heterogeneous porous media. They concentrated on understanding the
effect of the disposition of heterogeneous permeability on single-phase
flow for a known permeability distribution, determining if it is possible
to infer the presence and probable configuration of heterogeneities from
core analysis and conventional pressure transient tests. They showed that
the Lorenz coefficient can be correlated with the permeability variation
coefficient, as shown in Figure 3.47.
Averaging Techniques
There are three standard techniques used to estimate the average
permeability of a reservoir: arithmetic, geometric and harmonic.
(a) Arithmetic Average: The un-weighted arithmetic average permeability
k is determined from:
- ki
kA = - (3.116)
n
If the analysis of pressure transient tests yields much lower permeability
values than those obtained from core data, the lateral continuity of
the producing formation may not be sufficient to justify the arithmetic
averaging.