Page 571 - Petrophysics
P. 571
538 PETROPHYSICS: RESERVOIR ROCK PROPERTIES
i
i
I
I
I
I
100,000 10,000 1,000 100 10 1
At"= (tp + At)/At
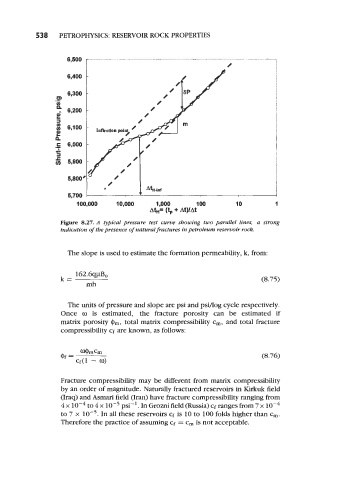
Figure 8.27. A typical pressure test curve showing two parallel lines, a strong
indication of the presence of natural fractures in petroleum reservoir rock.
The slope is used to estimate the formation permeability, k, from:
162 .6qyB0
k= (8.75)
mh
The units of pressure and slope are psi and psiflog cycle respectively.
Once o is estimated, the fracture porosity can be estimated if
matrix porosity @m, total matrix compressibility Cm, and total fracture
compressibility cf are known, as follows:
(8.76)
Fracture compressibility may be different from matrix compressibility
by an order of magnitude. Naturally fractured reservoirs in Kirkuk field
(Iraq) and Asmari field (Iran) have fracture compressibility ranging from
4 x to 4 x loy5 psi-'. In Grozni field (Russia) cf ranges from 7 x lop4
to 7 x In all these reservoirs cf is 10 to 100 folds higher than Cm.
Therefore the practice of assuming cf = Cm is not acceptable.