Page 106 - Physical chemistry understanding our chemical world
P. 106
CREATING FORMAL CHEMICAL BONDS 73
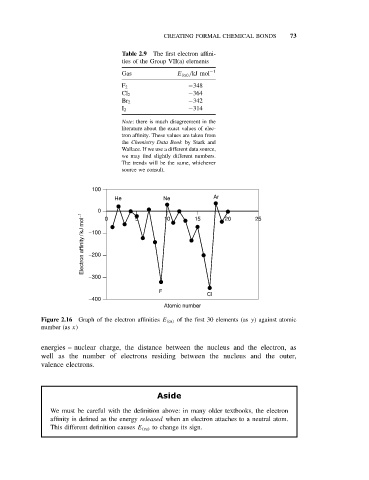
Table 2.9 The first electron affini-
ties of the Group VII(a) elements
Gas E (ea) /kJ mol −1
F 2 −348
Cl 2 −364
Br 2 −342
I 2 −314
Note: there is much disagreement in the
literature about the exact values of elec-
tron affinity. These values are taken from
the Chemistry Data Book by Stark and
Wallace. If we use a different data source,
we may find slightly different numbers.
The trends will be the same, whichever
source we consult.
100
He Ne Ar
0 0 5 10 15 20 25
Electron affinity / kJ mol −1 −100
−200
−300
F
CI
−400
Atomic number
Figure 2.16 Graph of the electron affinities E (ea) of the first 30 elements (as y) against atomic
number (as x)
energies – nuclear charge, the distance between the nucleus and the electron, as
well as the number of electrons residing between the nucleus and the outer,
valence electrons.
Aside
We must be careful with the definition above: in many older textbooks, the electron
affinity is defined as the energy released when an electron attaches to a neutral atom.
This different definition causes E (ea) to change its sign.