Page 207 - Physical chemistry understanding our chemical world
P. 207
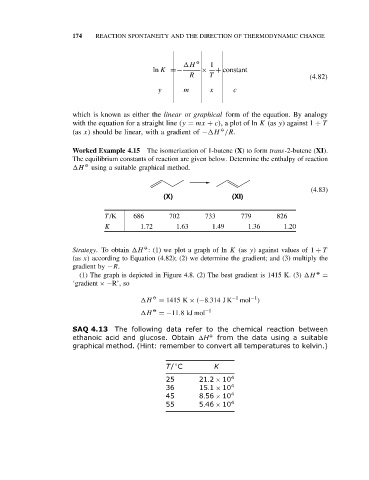
174 REACTION SPONTANEITY AND THE DIRECTION OF THERMODYNAMIC CHANGE
H O 1
ln K =− × + constant
R T (4.82)
y m x c
which is known as either the linear or graphical form of the equation. By analogy
with the equation for a straight line (y = mx + c), a plot of ln K (as y) against 1 ÷ T
O
(as x) should be linear, with a gradient of − H /R.
Worked Example 4.15 The isomerization of 1-butene (X)to form trans-2-butene (XI).
The equilibrium constants of reaction are given below. Determine the enthalpy of reaction
H O using a suitable graphical method.
(4.83)
(X) (XI)
T /K 686 702 733 779 826
K 1.72 1.63 1.49 1.36 1.20
O
Strategy. To obtain H : (1) we plot a graph of ln K (as y) against values of 1 ÷ T
(as x) according to Equation (4.82); (2) we determine the gradient; and (3) multiply the
gradient by −R.
(1) The graph is depicted in Figure 4.8. (2) The best gradient is 1415 K. (3) H O =
‘gradient ×−R’, so
−1
H O = 1415 K × (−8.314 J K −1 mol )
H O =−11.8kJ mol −1
SAQ 4.13 The following data refer to the chemical reaction between
ethanoic acid and glucose. Obtain H O from the data using a suitable
graphical method. (Hint: remember to convert all temperatures to kelvin.)
◦
T/ C K
25 21.2 × 10 4
36 15.1 × 10 4
45 8.56 × 10 4
55 5.46 × 10 4