Page 162 - Pipeline Risk Management Manual Ideas, Techniques, and Resources
P. 162
Product hazard 7/139
acute hazard
Chronic
model
Examples: I Is the product I
Benzene
Toluene
Butadiene volatile?
Chlorine
No
Examples: 4
Methane
Ethane Is a formal
cleanup required?
Propane lNo
Ethylene
Propylene Yes Fuel Examples:
oil
Diesel
Water
Nitrogen
1 Kerosene Hydrogen
f T Brine I
I
I 2R;ozooo RQ = 100 RQ = “none”
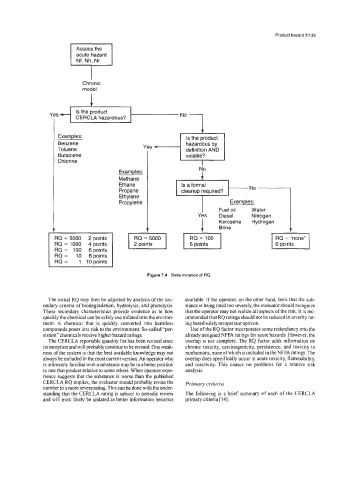
Figure 7.4 Determination of RQ
The initial RQ may then be adjusted by analysis of the sec- available. If the operator, on the other hand, feels that the sub-
ondary criteria of biodegradation, hydrolysis, and photolysis. stance is being rated too severely, the evaluator should recognize
These secondary characteristics provide evidence as to how that the operator may not realize all aspects of the risk. It is rec-
quickly the chemical can be safely assimilated into the environ- ommended that RQ ratings should not be reduced in severity rat-
ment. A chemical that is quickly converted into harmless ing based solely on operator opinion.
compounds poses less risk to the environment. So-called “per- Use of the RQ factor incorporates some redundancy into the
sistent” chemicals receive higher hazard ratings. already assigned NFPA ratings for acute hazards. However, the
The CERCLA reportable quantity list has been revised since overlap is not complete. The RQ factor adds information on
its inception and will probably continue to be revised. One weak- chronic toxicity, carcinogenicity, persistence, and toxicity to
ness of the system is that the best available knowledge may not nonhumans, none ofwhich is included in the NFPA ratings. The
always be included in the most current version. An operator who overlap does specifically occur in acute toxicity, flammability,
is intimately familiar with a substance may be in a better position and reactivity This causes no problems for a relative risk
to rate that product relative to some others. When operator expe- analysis.
rience suggests that the substance is worse than the published
CERCLA RQ implies, the evaluator should probably revise the Primary criteria
number to a more severe rating. This can be done with the under-
standing that the CERCLA rating is subject to periodic review The following is a brief summary of each of the CERCLA
and will most likely be updated as better information becomes primary criteria [ 141: