Page 235 - Pipeline Risk Management Manual Ideas, Techniques, and Resources
P. 235
101212 Service Interruption Risk
uses natural gas for cooking and home heating, the manufac- often contain 5 to 10% molecules heavier than methane (such
turer of the customers’ equipment (stove, heater, etc.) will as ethane, propane, butane, pentane, usually in that order) and
be the more reliable information source for contaminant the balance as methane molecules. A change in the amount
tolerances. andor the types of additional molecules in the methane could
The evaluator must assess potentials in all upstream sections change the gas Btu content and hence its burning characteris-
when scoring the possibility of contamination in a given tics. The majority of users of natural gas burn the gas, but Btu
section. General sources are identified as changes will rarely be a problem for them. Electrical power
generation plants often are more sensitive to Btu changes.
Product origin Hydrocarbon mix changes are commonly seen when the gas
0 Product equipment malfunctions source changes, perhaps from a different blending of pipeline
Pipeline dynamics supplies, different wells used, different gas compositions
Other. within a single well, or changes in the processing of the gas.
Many pipeline product streams are blends of several different
These sources are scored qualitatively here because general upstream product streams and hence are sensitive to the propor-
awarding ofpoints for all possible scenarios is usually not prac- tion mixture from the various streams.
tical. The evaluator is to judge, within guidelines set forth, the If the product source is a processing plant, the composition
potential for excursions from a specific source. To accomplish may depend on the processing variables and techniques.
this, the evaluator should have a clear understanding of the pos- Temperature, pressure, or catalyst changes within the process
sible excursion episodes. will change the resulting stream to varying extents. Materials
A list can be developed, based on customer specifications, used to remove impurities from a product stream may them-
that shows critical contaminants. Along with each potential selves introduce a contaminatior.. A carryover of glycol from a
contaminant, specific contaminant sources can be identified. dehydration unit is one example; an over-injection of a corro-
This list will serve as a prompter for the evaluator as assess- sion inhibitor is another. Inadequate processing is another
ments are made. An example is shown in Table 10.1. Optional source of contamination. A CO, scrubber in an LPG process-
columns such as detectability and sensitivity can be added to ing plant, for example, might occasionally allow an unaccept-
provide more guidance during the evaluation. This will also ably high level of CO, in the product stream to pass to the
serve to better document the assessment. pipeline.
Changes of products in storage facilities and pipeline
AI. Product origin change-in-service situations are potential sources of product
contamination. A composition change may also affect the den-
The possibility for contamination from the point ofproduct ori- sity, viscosity, and dew point of a gas stream. This can adversely
gin, including the potential for malfunction in the sourcing impact processes that are intolerant to liquid formation.
equipment, is considered here. If the product source is wells, The evaluator can develop a qualitative scale as follows to
tanks, reservoirs, processing plants, or pipelines not directly assess the contamination potential from changes at product
under the control of the operator, the operator of the sourcing origin.
facility must be relied on in part to prevent contamination.
One possible source of contamination in many hydrocarbon High 0 pts
products would be any radical change in the product’s hydro- Excursions are happening or have happened recently. Customer
carbon mix. Many product streams are composed of several impacts occur or are only narrowly avoided (near misses) by
hydrocarbons. Even a relatively pure natural gas stream will preventive actions.
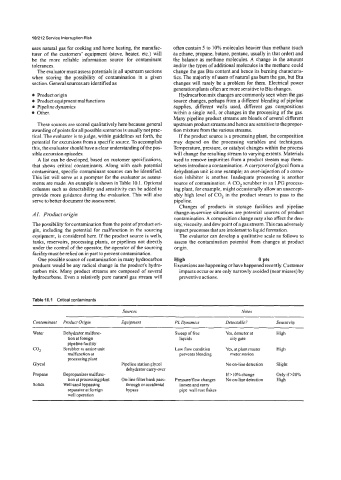
Table 10.1 Critical contaminants
Sources Notes
Contaminant Product Origin Equipment PL Dynamics Detectable? Sensitivity
Water Dehydrator malfunc- Sweep of free Yes, detector at High
tion at foreign liquids city gate
pipeline facility
CO, Scrubber or amine unit Low flow condition Yes, at plant master High
malfunction at prevents blending meter station
processing plant
Glycol Pipeline station glycol No on-line detection Slight
dehydrator carry-over
Propane Depropanizer malfunc- If>10% change Only if >20%
tion at processing plant On-line filter bank pass- Pressureiflow changes No on-line detection High
Solids Well sand bypassing through or accidental loosen and carry
separator at foreign bypass pipe wall rust flakes
well operation