Page 233 - Pipeline Risk Management Manual Ideas, Techniques, and Resources
P. 233
IO1210 Service Interruption Risk
‘failure potential’ variables has been added to the 400 points 4. Define potential consequences of service interruption.
already assigned to measure the relative probability of failure These consequences are normally expressed as monetary
due to excessive leakage. This sum is then modified by a conse- costs. They represent a separate component of the leak
quence factor. As in the basic risk assessment model, the impact factor.
numerical range is not very important-numbers are most
meaningful relative to other risk assessments. Some sections of pipeline are more critical than others in
terms of service interruption. In a distribution system, a service
main failure will impact many end customers, whereas a serv-
II. The process ice line failure will impact only a few. A transmission line fail-
ure might impact several entire distribution systems. A pipeline
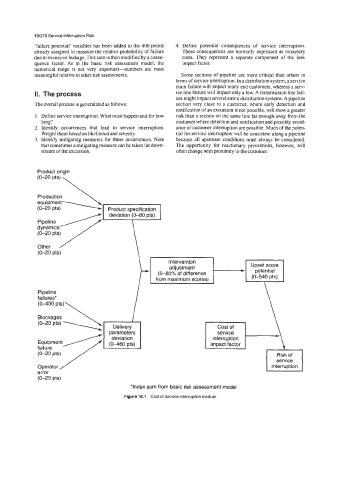
The overall process is generalized as follows: section very close to a customer, where early detection and
notification of an excursion is not possible, will show a greater
1. Define service interruption. What must happen and for how risk than a section on the same line far enough away from the
long? customer where detection and notification and possibly avoid-
2. Identify OccUrrences that lead to service interruption. ance of customer interruption are possible. Much of the poten-
Weight these based on likelihood and severity. tial for service interruption will be consistent along a pipeline
3. Identify mitigating measures for these occurrences. Note because all upstream conditions must always be considered.
that sometimes a mitigating measure can be taken far down- The opportunity for reactionary preventions, however, will
stream of the excursion. often change with proximity to the customer.
Product origin
(0-20 pts)
Production
Pipeline
dynamics
(0-20 pts)
Other / \
(0-20 pts)
(0-80% of difference
from maximum scores)
Pipeline
failures* I
Blockages \ I
parameters service
deviation
/
Operator / service
error
(0-20 pts)
‘Index sum from basic risk assessment model
Figure 10.1 Cost of service interruption module.