Page 253 - Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook
P. 253
240 Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook
molecular weight is not known or cannot be readily deter- Example. If the molecular weight of the gas in the
mined. This may be accomplished if the specific gravity of the preceding example was unknown, but the specific gravity
gas is known by using the formula: was known to be 0.581, substitution in the formula would
give:
GVp
.
W = 2 698 ¥ (7)
T
0 581 ¥ 1 000 ¥ (150 14 3 )
,
.
.
+
where G = the specific gravity of the gas (air equals 1.000) W = 2 698 ¥
.
and the other symbols and units are as previously (90 + 460 )
.
given = 468 3 lb
Calculate gas properties from a gas analysis
In most practical applications involving gas calculations, the Therefore, the properties of the mix will be:
gas will consist of a mixture of components. Properties of the
components are known; however, the properties of the mix Molecular weight = MW = 45.5
must be determined for use in other calculations, such as Critical pressure = P c = 611
compressor performance calculations. The gas molecular Critical temperature = T c = 676
weight, K-value (isentropic exponent), and compressibility of Specific heat at constant pressure = cp = 17.76
the gas mix will be determined in the calculation to follow.
The ratio of specific heats for the mixture are calculated
Other data that may be needed for compressor performance
from Equation 1.
determination will likely come from the process design and
from the manufacturer’s data.
.
k mix = cp mix ( cp mix - 1 986 ) (1)
Sample calculation 1 k mix = 17 76 (17 76. - 1 986 )
.
.
= 1 126
.
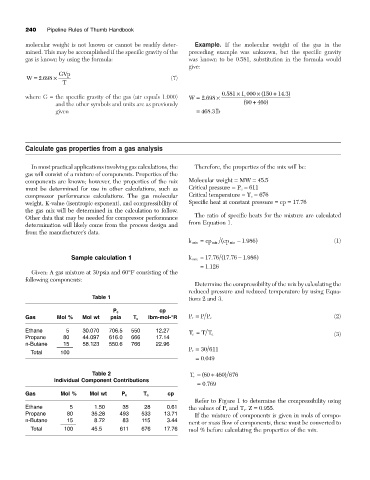
Given: A gas mixture at 30psia and 60°F consisting of the
following components:
Determine the compressibility of the mix by calculating the
reduced pressure and reduced temperature by using Equa-
Table 1 tions 2 and 3.
cp
P c
Gas Mol % Mol wt psia T c Ibm-mol-°R P r = P P c (2)
Ethane 5 30.070 706.5 550 12.27
T r = T T c (3)
Propane 80 44.097 616.0 666 17.14
n-Butane 15 58.123 550.6 766 22.96
P r = 30 611
Total 100
.
= 0 049
Table 2 T r = (60 460 676
)
+
Individual Component Contributions
.
= 0 769
Gas Mol % Mol wt P c T c cp
Refer to Figure 1 to determine the compressibility using
Ethane 5 1.50 35 28 0.61 the values of P r and T r . Z = 0.955.
Propane 80 35.28 493 533 13.71 If the mixture of components is given in mols of compo-
n-Butane 15 8.72 83 115 3.44
nent or mass flow of components, these must be converted to
Total 100 45.5 611 676 17.76 mol % before calculating the properties of the mix.