Page 148 - Plant design and economics for chemical engineers
P. 148
COMPUTER-AIDED DESIGN 123
Fuel gas Water
3.6 lb/h 536 lb/h
I
Liquid
EB recycle, 112.6 lb/h
Tcc)
Styrene
prbduct
104 lb/h
T a r
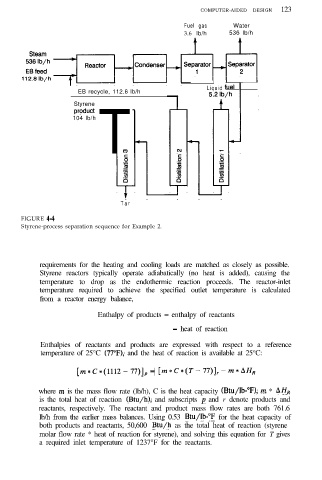
FIGURE 4-4
Styrene-process separation sequence for Example 2.
requirements for the heating and cooling loads are matched as closely as possible.
Styrene reactors typically operate adiabatically (no heat is added), causing the
temperature to drop as the endothermic reaction proceeds. The reactor-inlet
temperature required to achieve the specified outlet temperature is calculated
from a reactor energy balance,
Enthalpy of products = enthalpy of reactants
- heat of reaction
Enthalpies of reactants and products are expressed with respect to a reference
temperature of 25°C (77”F), and the heat of reaction is available at 25°C:
[m*C*(1112-77)],= [m*C*(T-77)],-m*AH,
where m is the mass flow rate (lb/h), C is the heat capacity (Btu/lb-“F), m * AH,
is the total heat of reaction (Btu/h), and subscripts p and r denote products and
reactants, respectively. The reactant and product mass flow rates are both 761.6
lb/h from the earlier mass balances. Using 0.53 Btu/lb-“F for the heat capacity of
both products and reactants, 50,600 Btu/h as the total heat of reaction (styrene
molar flow rate * heat of reaction for styrene), and solving this equation for T gives
a required inlet temperature of 1237°F for the reactants.