Page 23 - Plant-Based Remediation Processes
P. 23
10 S. Chatterjee et al.
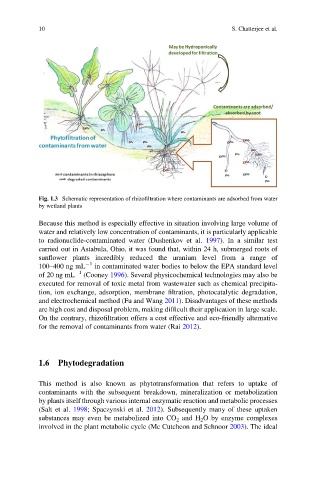
Fig. 1.3 Schematic representation of rhizofiltration where contaminants are adsorbed from water
by wetland plants
Because this method is especially effective in situation involving large volume of
water and relatively low concentration of contaminants, it is particularly applicable
to radionuclide-contaminated water (Dushenkov et al. 1997). In a similar test
carried out in Astabula, Ohio, it was found that, within 24 h, submerged roots of
sunflower plants incredibly reduced the uranium level from a range of
100–400 ng mL 1 in contaminated water bodies to below the EPA standard level
of 20 ng mL 1 (Cooney 1996). Several physicochemical technologies may also be
executed for removal of toxic metal from wastewater such as chemical precipita-
tion, ion exchange, adsorption, membrane filtration, photocatalytic degradation,
and electrochemical method (Fu and Wang 2011). Disadvantages of these methods
are high cost and disposal problem, making difficult their application in large scale.
On the contrary, rhizofiltration offers a cost effective and eco-friendly alternative
for the removal of contaminants from water (Rai 2012).
1.6 Phytodegradation
This method is also known as phytotransformation that refers to uptake of
contaminants with the subsequent breakdown, mineralization or metabolization
by plants itself through various internal enzymatic reaction and metabolic processes
(Salt et al. 1998; Spaczynski et al. 2012). Subsequently many of these uptaken
substances may even be metabolized into CO 2 and H 2 O by enzyme complexes
involved in the plant metabolic cycle (Mc Cutcheon and Schnoor 2003). The ideal