Page 145 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 145
120 Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
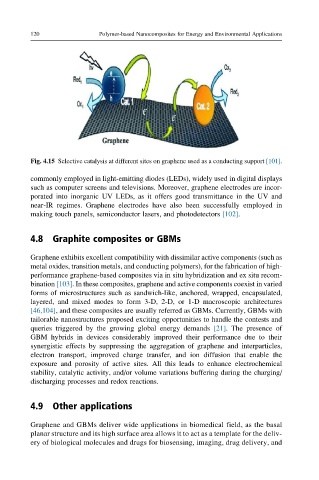
Fig. 4.15 Selective catalysis at different sites on graphene used as a conducting support [101].
commonly employed in light-emitting diodes (LEDs), widely used in digital displays
such as computer screens and televisions. Moreover, graphene electrodes are incor-
porated into inorganic UV LEDs, as it offers good transmittance in the UV and
near-IR regimes. Graphene electrodes have also been successfully employed in
making touch panels, semiconductor lasers, and photodetectors [102].
4.8 Graphite composites or GBMs
Graphene exhibits excellent compatibility with dissimilar active components (such as
metal oxides, transition metals, and conducting polymers), for the fabrication of high-
performance graphene-based composites via in situ hybridization and ex situ recom-
bination [103]. In these composites, graphene and active components coexist in varied
forms of microstructures such as sandwich-like, anchored, wrapped, encapsulated,
layered, and mixed modes to form 3-D, 2-D, or 1-D macroscopic architectures
[46,104], and these composites are usually referred as GBMs. Currently, GBMs with
tailorable nanostructures proposed exciting opportunities to handle the contests and
queries triggered by the growing global energy demands [21]. The presence of
GBM hybrids in devices considerably improved their performance due to their
synergistic effects by suppressing the aggregation of graphene and interparticles,
electron transport, improved charge transfer, and ion diffusion that enable the
exposure and porosity of active sites. All this leads to enhance electrochemical
stability, catalytic activity, and/or volume variations buffering during the charging/
discharging processes and redox reactions.
4.9 Other applications
Graphene and GBMs deliver wide applications in biomedical field, as the basal
planar structure and its high surface area allows it to act as a template for the deliv-
ery of biological molecules and drugs for biosensing, imaging, drug delivery, and