Page 144 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 144
Energy and environmental applications of graphene and its derivatives 119
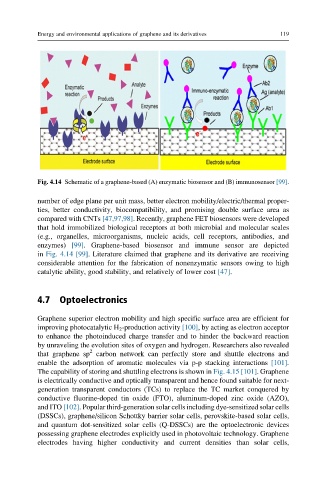
Fig. 4.14 Schematic of a graphene-based (A) enzymatic biosensor and (B) immunosensor [99].
number of edge plane per unit mass, better electron mobility/electric/thermal proper-
ties, better conductivity, biocompatibility, and promising double surface area as
compared with CNTs [47,97,98]. Recently, graphene FET biosensors were developed
that hold immobilized biological receptors at both microbial and molecular scales
(e.g., organelles, microorganisms, nucleic acids, cell receptors, antibodies, and
enzymes) [99]. Graphene-based biosensor and immune sensor are depicted
in Fig. 4.14 [99]. Literature claimed that graphene and its derivative are receiving
considerable attention for the fabrication of nonenzymatic sensors owing to high
catalytic ability, good stability, and relatively of lower cost [47].
4.7 Optoelectronics
Graphene superior electron mobility and high specific surface area are efficient for
improving photocatalytic H 2 -production activity [100], by acting as electron acceptor
to enhance the photoinduced charge transfer and to hinder the backward reaction
by unraveling the evolution sites of oxygen and hydrogen. Researchers also revealed
2
that graphene sp carbon network can perfectly store and shuttle electrons and
enable the adsorption of aromatic molecules via p-p stacking interactions [101].
The capability of storing and shuttling electrons is shown in Fig. 4.15 [101]. Graphene
is electrically conductive and optically transparent and hence found suitable for next-
generation transparent conductors (TCs) to replace the TC market conquered by
conductive fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO), aluminum-doped zinc oxide (AZO),
and ITO [102]. Popular third-generation solar cells including dye-sensitized solar cells
(DSSCs), graphene/silicon Schottky barrier solar cells, perovskite-based solar cells,
and quantum dot-sensitized solar cells (Q-DSSCs) are the optoelectronic devices
possessing graphene electrodes explicitly used in photovoltaic technology. Graphene
electrodes having higher conductivity and current densities than solar cells,