Page 356 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 356
Modification of polymer nanocomposites and significance of ionic liquid 323
11.8.3.1 Carbon nanotubes
2
Carbon nanotubes are almost one-dimensional sp -bonded single graphite sheet
encased in cylindrical structure that can be incorporated as single-walled nanotubes
or multiwalled nanotubes. Due to its amazing mechanical and electronic properties,
carbon nanotubes have grasped the interest of analyst globally. It has an elastic mod-
ulus that is greater than diamond, which is one of the hardest materials.
In current days, carbon nanotubes have been projected as electrode supplies for
supercapacitors, one of various possible applications of carbon nanotubes, others
being photovoltaic cells, Li-ion secondary batteries, and hydrogen storage in fuel
cells. The exclusive properties of carbon nanotubes, such as high surface area, struc-
ture (one-dimensional geometry), high electric conductivity, significant chemical sta-
bility, and light weight have determined its use in storage application and energy
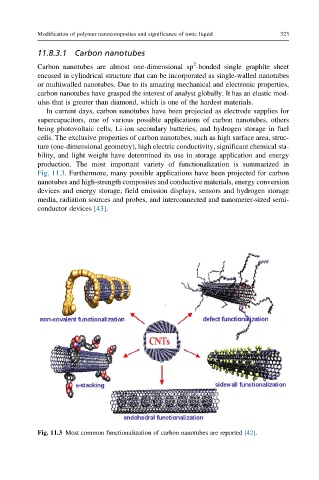
production. The most important variety of functionalization is summarized in
Fig. 11.3. Furthermore, many possible applications have been projected for carbon
nanotubes and high-strength composites and conductive materials, energy conversion
devices and energy storage, field emission displays, sensors and hydrogen storage
media, radiation sources and probes, and interconnected and nanometer-sized semi-
conductor devices [43].
Fig. 11.3 Most common functionalization of carbon nanotubes are reported [42].