Page 359 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 359
326 Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
Cooling technology
Sorption cooling media
Heat transort and storage Separation technology
Thermal fluids Phase changing materials
Phase changing materials Thermal fluids
Ionic liquids
• High thermal stability
Functional fluids • High ionic conductivity Synthesis and catalysis
Lubricants Enzymatic reaction
• Low vapor pressure
Surfactants • Tuneable miscibility Nano-particle synthesis
Hydraulic oil • Electrochemical stability lmmobolization of catalysis
Storage media for gases Solvent for organic reaction
• Relative low viscosity
• High solvating capacity
• Non-flammability
Analytics Electrolytes
Electrophoresis Sensor
Solvent for GC head space Fuel cells
Solvent for Karl Fischer titration Super capacitor
Solvent for protein crystallization Metal deposition
Matrix materials for MALDI-TOF-MS Dye sensitized solar cells
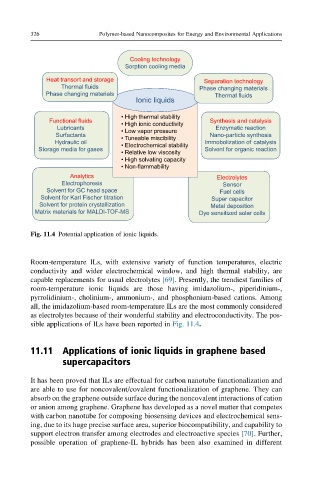
Fig. 11.4 Potential application of ionic liquids.
Room-temperature ILs, with extensive variety of function temperatures, electric
conductivity and wider electrochemical window, and high thermal stability, are
capable replacements for usual electrolytes [69]. Presently, the trendiest families of
room-temperature ionic liquids are those having imidazolium-, piperidinium-,
pyrrolidinium-, cholinium-, ammonium-, and phosphonium-based cations. Among
all, the imidazolium-based room-temperature ILs are the most commonly considered
as electrolytes because of their wonderful stability and electroconductivity. The pos-
sible applications of ILs have been reported in Fig. 11.4.
11.11 Applications of ionic liquids in graphene based
supercapacitors
It has been proved that ILs are effectual for carbon nanotube functionalization and
are able to use for noncovalent/covalent functionalization of graphene. They can
absorb on the graphene outside surface during the noncovalent interactions of cation
or anion among graphene. Graphene has developed as a novel matter that competes
with carbon nanotube for composing biosensing devices and electrochemical sens-
ing, due to its huge precise surface area, superior biocompatibility, and capability to
support electron transfer among electrodes and electroactive species [70].Further,
possible operation of graphene-IL hybrids has been also examined in different