Page 418 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 418
Polymer nanocomposites for dye-sensitized solar cells 375
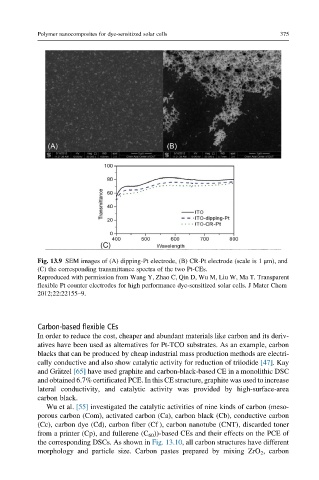
Fig. 13.9 SEM images of (A) dipping-Pt electrode, (B) CR-Pt electrode (scale is 1 μm), and
(C) the corresponding transmittance spectra of the two Pt-CEs.
Reproduced with permission from Wang Y, Zhao C, Qin D, Wu M, Liu W, Ma T. Transparent
flexible Pt counter electrodes for high performance dye-sensitized solar cells. J Mater Chem
2012;22:22155–9.
Carbon-based flexible CEs
In order to reduce the cost, cheaper and abundant materials like carbon and its deriv-
atives have been used as alternatives for Pt-TCO substrates. As an example, carbon
blacks that can be produced by cheap industrial mass production methods are electri-
cally conductive and also show catalytic activity for reduction of triiodide [47]. Kay
and Gr€ atzel [65] have used graphite and carbon-black-based CE in a monolithic DSC
and obtained 6.7% certificated PCE. In this CE structure, graphite was used to increase
lateral conductivity, and catalytic activity was provided by high-surface-area
carbon black.
Wu et al. [55] investigated the catalytic activities of nine kinds of carbon (meso-
porous carbon (Com), activated carbon (Ca), carbon black (Cb), conductive carbon
(Cc), carbon dye (Cd), carbon fiber (Cf ), carbon nanotube (CNT), discarded toner
from a printer (Cp), and fullerene (C 60 ))-based CEs and their effects on the PCE of
the corresponding DSCs. As shown in Fig. 13.10, all carbon structures have different
morphology and particle size. Carbon pastes prepared by mixing ZrO 2 , carbon