Page 458 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 458
Nanocomposite membrane for environmental remediation 415
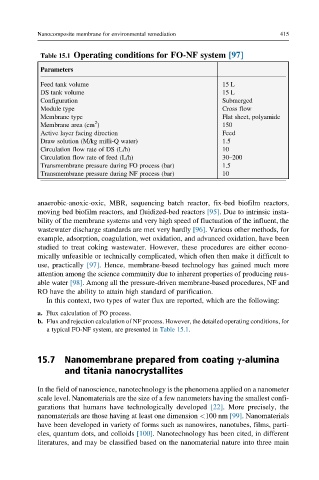
Table 15.1 Operating conditions for FO-NF system [97]
Parameters
Feed tank volume 15 L
DS tank volume 15 L
Configuration Submerged
Module type Cross flow
Membrane type Flat sheet, polyamide
2
Membrane area (cm ) 150
Active layer facing direction Feed
Draw solution (M/kg milli-Q water) 1.5
Circulation flow rate of DS (L/h) 10
Circulation flow rate of feed (L/h) 30–200
Transmembrane pressure during FO process (bar) 1.5
Transmembrane pressure during NF process (bar) 10
anaerobic-anoxic-oxic, MBR, sequencing batch reactor, fix-bed biofilm reactors,
moving bed biofilm reactors, and fluidized-bed reactors [95]. Due to intrinsic insta-
bility of the membrane systems and very high speed of fluctuation of the influent, the
wastewater discharge standards are met very hardly [96]. Various other methods, for
example, adsorption, coagulation, wet oxidation, and advanced oxidation, have been
studied to treat coking wastewater. However, these procedures are either econo-
mically unfeasible or technically complicated, which often then make it difficult to
use, practically [97]. Hence, membrane-based technology has gained much more
attention among the science community due to inherent properties of producing reus-
able water [98]. Among all the pressure-driven membrane-based procedures, NF and
RO have the ability to attain high standard of purification.
In this context, two types of water flux are reported, which are the following:
a. Flux calculation of FO process.
b. Flux and rejection calculation of NF process. However, the detailed operating conditions, for
a typical FO-NF system, are presented in Table 15.1.
15.7 Nanomembrane prepared from coating γ-alumina
and titania nanocrystallites
In the field of nanoscience, nanotechnology is the phenomena applied on a nanometer
scale level. Nanomaterials are the size of a few nanometers having the smallest confi-
gurations that humans have technologically developed [22]. More precisely, the
nanomaterials are those having at least one dimension <100 nm [99]. Nanomaterials
have been developed in variety of forms such as nanowires, nanotubes, films, parti-
cles, quantum dots, and colloids [100]. Nanotechnology has been cited, in different
literatures, and may be classified based on the nanomaterial nature into three main