Page 462 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 462
[114]
[112]
[113]
Ref.
within
but the only problem of drop in flux and
dairy
controlled,
role
expensive
vital
quality
of
(AgTiO 2 )
of
degradation
with
a
is
be
play
water
best
less
technique
can
compared
nanomaterials
membrane
method,
standards
and
treated
fouling
required
photocatalytic
water
efficient
conventional
as
of
recycle
Observations
Membrane
recyclable
permeates
technique
nanofiber
chemical
level
wastes,
More
For
the
In
treatment
l
l
l
l
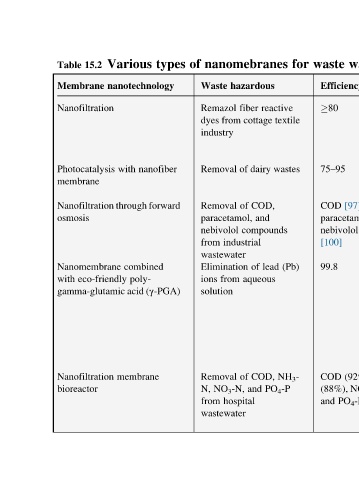
compounds
and
(%)
water
paracetamol,
Efficiency
[97],
nebivolol
75–95
waste Nanocomposite membrane for environmental remediation l [75] Pb 2+ with binds γ-PGA Eco-friendly 99.8 and fast filtered be can and ions of combination with effectively using filtration fast and nanomembrane γ-PGA cross-linked or linear optimal with technology biopolymer removal Pb 2+ l WHO meets
[100]
COD
80
for reactive textile wastes (Pb) NH 3 - PO 4 -P
nanomebranes hazardous fiber cottage from dairy of COD, of and paracetamol, compounds industrial wastewater lead of Elimination aqueous from COD, of and NO 3 -N, hospital wastewater
of Waste Remazol dyes industry Removal Removal nebivolol from ions solution Removal N, from
types nanofiber
Various nanotechnology with Nanofiltration through forward combined poly- gamma-glutamic acid (γ-PGA) membrane
15.2 Nanofiltration Photocatalysis Nanomembrane eco-friendly Nanofiltration
Table Membrane membrane osmosis with bioreactor