Page 465 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 465
420 Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
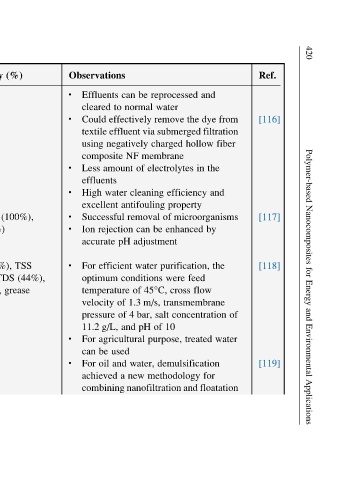
Ref. [116] [117] [118] [119]
from fiber of water
and dye the submerged filtration hollow the in and microorganisms by the feed flow transmembrane concentration treated for
reprocessed water remove charged membrane electrolytes efficiency property of enhanced purification, were cross salt 10 purpose, demulsification methodology combining nanofiltration and floatation
be normal via of cleaning antifouling removal be can adjustment water conditions 45°C, of m/s, bar, of pH water,
can to effectively effluent negatively NF amount water rejection pH efficient 1.3 of 4 of and agricultural used and new a
Observations l Effluents cleared l Could textile using composite l Less effluents l High excellent l Successful l Ion accurate l For optimum temperature velocity pressure g/L, 11.2 l For be can l oil For achieved
(%) (100%), TSS (76%), (44%), TDS grease
Efficiency 99% Microbes (25%) ions BOD (100%), (99%), oil (80%) 99.75%
dye ion and BOD,
hazardous reactive of textile from of microorganisms from COD, of and oil, TDS, oil from removal
Waste Removal 5 black effluent Removal rejection wastewater Removal TSS, grease wastewater oil For
Continued nanotechnology membranes from prepared titania and membrane Nanostructured polymer-based
15.2 Nanofiltration Nanomembrane γ-alumina nanocrystallites
Table Membrane coating Nanoporous filtration membrane