Page 564 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 564
Hybrid materials based on polymer nanocomposites for environmental applications 517
Polymer chains
Polymer chains
Si O Si
O
O O O
Polymer chains
Si O Si Polymer chains
Si O Si
Polymer chains O O
O O
Si O Si Polymer chains
Polymer chains Polymer chains
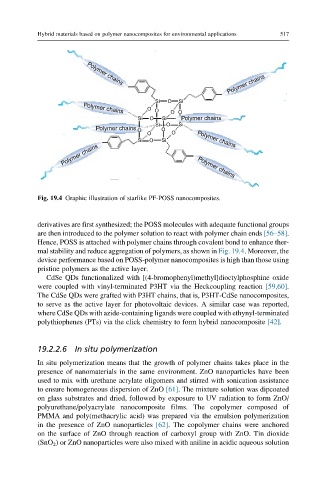
Fig. 19.4 Graphic illustration of starlike PF-POSS nanocomposites.
derivatives are first synthesized; the POSS molecules with adequate functional groups
are then introduced to the polymer solution to react with polymer chain ends [56–58].
Hence, POSS is attached with polymer chains through covalent bond to enhance ther-
mal stability and reduce aggregation of polymers, as shown in Fig. 19.4. Moreover, the
device performance based on POSS-polymer nanocomposites is high than those using
pristine polymers as the active layer.
CdSe QDs functionalized with [(4-bromophenyl)methyl]dioctylphosphine oxide
were coupled with vinyl-terminated P3HT via the Heckcoupling reaction [59,60].
The CdSe QDs were grafted with P3HT chains, that is, P3HT-CdSe nanocomposites,
to serve as the active layer for photovoltaic devices. A similar case was reported,
where CdSe QDs with azide-containing ligands were coupled with ethynyl-terminated
polythiophenes (PTs) via the click chemistry to form hybrid nanocomposite [42].
19.2.2.6 In situ polymerization
In situ polymerization means that the growth of polymer chains takes place in the
presence of nanomaterials in the same environment. ZnO nanoparticles have been
used to mix with urethane acrylate oligomers and stirred with sonication assistance
to ensure homogeneous dispersion of ZnO [61]. The mixture solution was dipcoated
on glass substrates and dried, followed by exposure to UV radiation to form ZnO/
polyurethane/polyacrylate nanocomposite films. The copolymer composed of
PMMA and poly(methacrylic acid) was prepared via the emulsion polymerization
in the presence of ZnO nanoparticles [62]. The copolymer chains were anchored
on the surface of ZnO through reaction of carboxyl group with ZnO. Tin dioxide
(SnO 2 ) or ZnO nanoparticles were also mixed with aniline in acidic aqueous solution