Page 576 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 576
Hybrid materials based on polymer nanocomposites for environmental applications 529
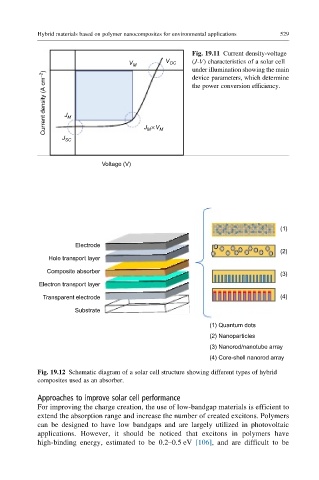
Fig. 19.11 Current density-voltage
V M V OC (J-V) characteristics of a solar cell
under illumination showing the main
Current density (A cm −2 ) J M
device parameters, which determine
the power conversion efficiency.
M
J SC J × V M
Voltage (V)
(1)
Electrode
(2)
Hole transport layer
Composite absorber
(3)
Electron transport layer
Transparent electrode (4)
Substrate
(1) Quantum dots
(2) Nanoparticles
(3) Nanorod/nanotube array
(4) Core-shell nanorod array
Fig. 19.12 Schematic diagram of a solar cell structure showing different types of hybrid
composites used as an absorber.
Approaches to improve solar cell performance
For improving the charge creation, the use of low-bandgap materials is efficient to
extend the absorption range and increase the number of created excitons. Polymers
can be designed to have low bandgaps and are largely utilized in photovoltaic
applications. However, it should be noticed that excitons in polymers have
high-binding energy, estimated to be 0.2–0.5 eV [106], and are difficult to be