Page 578 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 578
Hybrid materials based on polymer nanocomposites for environmental applications 531
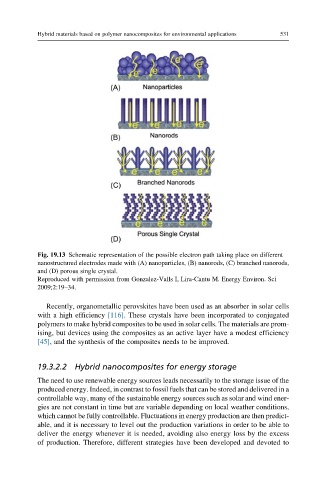
Fig. 19.13 Schematic representation of the possible electron path taking place on different
nanostructured electrodes made with (A) nanoparticles, (B) nanorods, (C) branched nanorods,
and (D) porous single crystal.
Reproduced with permission from Gonzalez-Valls I, Lira-Cantu M. Energy Environ. Sci
2009;2:19–34.
Recently, organometallic perovskites have been used as an absorber in solar cells
with a high efficiency [116]. These crystals have been incorporated to conjugated
polymers to make hybrid composites to be used in solar cells. The materials are prom-
ising, but devices using the composites as an active layer have a modest efficiency
[45], and the synthesis of the composites needs to be improved.
19.3.2.2 Hybrid nanocomposites for energy storage
The need to use renewable energy sources leads necessarily to the storage issue of the
produced energy. Indeed, in contrast to fossil fuels that can be stored and delivered in a
controllable way, many of the sustainable energy sources such as solar and wind ener-
gies are not constant in time but are variable depending on local weather conditions,
which cannot be fully controllable. Fluctuations in energy production are then predict-
able, and it is necessary to level out the production variations in order to be able to
deliver the energy whenever it is needed, avoiding also energy loss by the excess
of production. Therefore, different strategies have been developed and devoted to