Page 81 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 81
Preparation and properties of nanopolymer advanced composites: A review 57
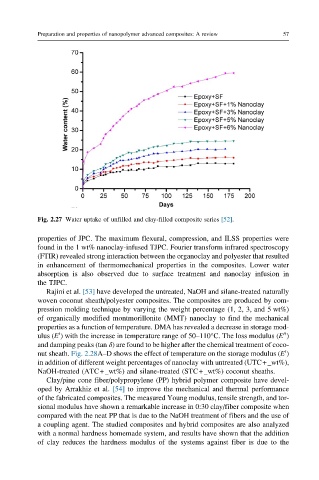
Fig. 2.27 Water uptake of unfilled and clay-filled composite series [52].
properties of JPC. The maximum flexural, compression, and ILSS properties were
found in the 1 wt% nanoclay-infused TJPC. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
(FTIR) revealed strong interaction between the organoclay and polyester that resulted
in enhancement of thermomechanical properties in the composites. Lower water
absorption is also observed due to surface treatment and nanoclay infusion in
the TJPC.
Rajini et al. [53] have developed the untreated, NaOH and silane-treated naturally
woven coconut sheath/polyester composites. The composites are produced by com-
pression molding technique by varying the weight percentage (1, 2, 3, and 5 wt%)
of organically modified montmorillonite (MMT) nanoclay to find the mechanical
properties as a function of temperature. DMA has revealed a decrease in storage mod-
ulus (E ) with the increase in temperature range of 50–110°C. The loss modulus (E )
0
00
and damping peaks (tan δ) are found to be higher after the chemical treatment of coco-
nut sheath. Fig. 2.28A–D shows the effect of temperature on the storage modulus (E )
0
in addition of different weight percentages of nanoclay with untreated (UTC+_wt%),
NaOH-treated (ATC+_wt%) and silane-treated (STC+_wt%) coconut sheaths.
Clay/pine cone fiber/polypropylene (PP) hybrid polymer composite have devel-
oped by Arrakhiz et al. [54] to improve the mechanical and thermal performance
of the fabricated composites. The measured Young modulus, tensile strength, and tor-
sional modulus have shown a remarkable increase in 0:30 clay/fiber composite when
compared with the neat PP that is due to the NaOH treatment of fibers and the use of
a coupling agent. The studied composites and hybrid composites are also analyzed
with a normal hardness homemade system, and results have shown that the addition
of clay reduces the hardness modulus of the systems against fiber is due to the