Page 85 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 85
Preparation and properties of nanopolymer advanced composites: A review 61
28
TJPCC
TJPC
26
RJPCC
Tensile strength (MPa) 22
RJPC
24
20
18
16
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
(A) Fiber loadings (wt%)
1.6
TJPCC
TJPC
Tensile modulus (GPa) 0.8
RJPCC
1.2
RJPC
0.4
0 5 10 15 20
(B) Fiber loadings (wt%)
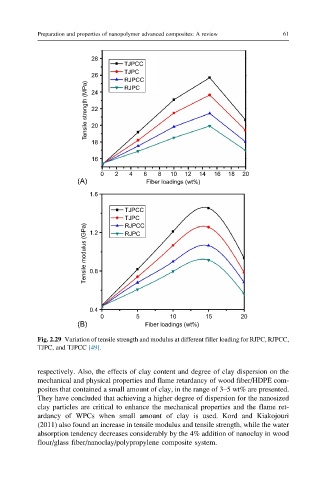
Fig. 2.29 Variation of tensile strength and modulus at different filler loading for RJPC, RJPCC,
TJPC, and TJPCC [49].
respectively. Also, the effects of clay content and degree of clay dispersion on the
mechanical and physical properties and flame retardancy of wood fiber/HDPE com-
posites that contained a small amount of clay, in the range of 3–5 wt% are presented.
They have concluded that achieving a higher degree of dispersion for the nanosized
clay particles are critical to enhance the mechanical properties and the flame ret-
ardancy of WPCs when small amount of clay is used. Kord and Kiakojouri
(2011) also found an increase in tensile modulus and tensile strength, while the water
absorption tendency decreases considerably by the 4% addition of nanoclay in wood
flour/glass fiber/nanoclay/polypropylene composite system.