Page 117 - Power Quality in Electrical Systems
P. 117
100 Chapter Seven
Conducted EMI can also result in radiated noise, since a primary
source of radiated EMI is current in the AC power leads. In recent years,
the United States and Europe have placed stringent requirements on
the harmonic pollution injected into power lines. In this chapter, we will
discuss high-frequency power supply issues and other technical chal-
lenges related to harmonic injection and EMI.
Offline Power Supplies
Offline power supplies are a class of supplies supplied by the AC line,
and generally produce one or more DC outputs. The input AC source is
rectified, and the resultant rectified voltage is chopped at a high fre-
quency to produce the desired DC output(s). The load presented by the
input rectifier is a large capacitor, so the line current is therefore highly
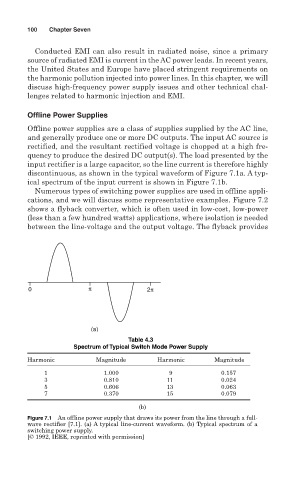
discontinuous, as shown in the typical waveform of Figure 7.1a. A typ-
ical spectrum of the input current is shown in Figure 7.1b.
Numerous types of switching power supplies are used in offline appli-
cations, and we will discuss some representative examples. Figure 7.2
shows a flyback converter, which is often used in low-cost, low-power
(less than a few hundred watts) applications, where isolation is needed
between the line-voltage and the output voltage. The flyback provides
0 π 2π
(a)
Table 4.3
Spectrum of Typical Switch Mode Power Supply
Harmonic Magnitude Harmonic Magnitude
1 1.000 9 0.157
3 0.810 11 0.024
5 0.606 13 0.063
7 0.370 15 0.079
(b)
Figure 7.1 An offline power supply that draws its power from the line through a full-
wave rectifier [7.1]. (a) A typical line-current waveform. (b) Typical spectrum of a
switching power supply.
[© 1992, IEEE, reprinted with permission]