Page 179 - Practical Design Ships and Floating Structures
P. 179
154
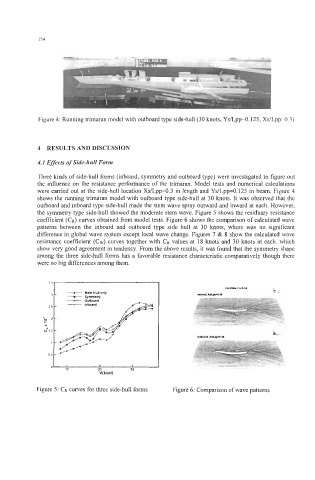
Figure 4: Running trimaran model with outboard type side-hull (30 knots, Ys/Lpp=O. 125, Xs/Lpp=O.3)
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Effects of Side-hull Form
Three kinds of side-hull forms (inboard, symmetry and outboard type) were investigated to figure out
the influence on the resistance performance of the trimaran. Model tests and numerical calculations
were carried out at the side-hull location Xs/Lpp=O.3 in length and Ys/Lpp=O.125 in beam. Figure 4
shows the running trimaran model with outboard type side-hull at 30 knots. It was observed that the
outboard and inboard type side-hull made the stem wave spray outward and inward at each. However,
the symmetry type side-hull showed the moderate stem wave. Figure 5 shows the residuary resistance
coefficient (CR) curves obtained from model tests. Figure 6 shows the comparison of calculated wave
patterns between the inboard and outboard type side hull at 30 knots, where was no significant
difference in global wave system except local wave change. Figures 7 & 8 show the calculated wave
resistance coefficient (CW) curves together with CR values at 18 knots and 30 knots at each, which
show very good agreement in tendency. From the above results, it was found that the symmetry shape
among the three side-hull forms has a favorable resistance characteristic comparatively though there
were no big differences among them.
Figure 5: CR curves for three side-hull forms Figure 6: Comparison of wave patterns