Page 444 - Practical Design Ships and Floating Structures
P. 444
419
.on, I 1 .'
J.5 -11.25 11 u 2s us .I
In
0.03
0.1125
0.02
0.0,5
11.0,
0.005
0
-0.oDI
.o.u*
4s .O.ZS a 0.2s OS
rn
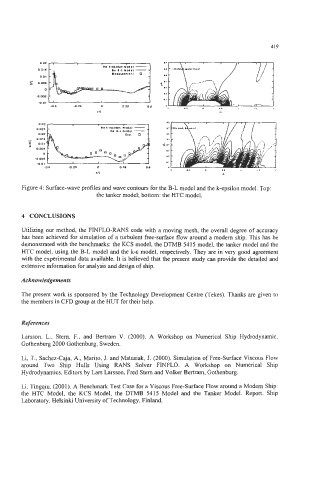
Figure 4: Surface-wave profiles and wave contours for the B-L model and the k-epsilon model. Top:
the tanker model; bottom: the HTC model.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Utilizing our method, the FINFLO-RANS code with a moving mesh, the overall degree of accuracy
has been achieved for simulation of a turbulent free-surface flow around a modem ship. This has be
demonstrated with the benchmarks: the KCS model, the DTMB 541 5 model, the tanker model and the
HTC model. using the B-L model and the k-E model, respectively. They are in very good agreement
with the experimental data available. It is believed that the present study can provide the detailed and
extensive information for analysis and design of ship.
Acknowledgements
The present work is sponsored by the Technology Development Centre (Tekes). Thanks are given IO
the members in CFD group at the HUT for their help.
References
Larsson. L.. Stem, F., and Bertram V. (2000). A Workshop on Numerical Ship Hydrodynamic.
Gothenburg 2000 Gothenburg, Sweden.
Li, T., Sachez-Caja, A., Marito, J. and Matusiak. J. (2000). Simulation of Free-Surface Viscous Flow
around Two Ship Hulls Using RANS Solver FINFLO. A Workshop on Numerical Ship
Hydrodynamics, Editors by Lars Larsson. Fred Stern and Volker Bertram, Gothenburg.
Li. Tingqiu. (2001). A Benchmark Test Case for a Viscous Free-Surface Flow around a Modern Ship:
the HTC Model, the KCS Model, the DTMB 5415 Model and the Tanker Model. Report. Ship
Laboratory. Helsinki University of Technology, Finland.