Page 487 - Practical Design Ships and Floating Structures
P. 487
462
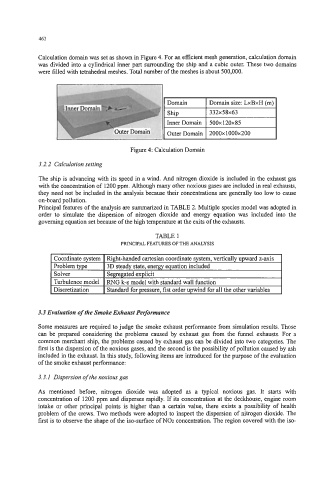
Calculation domain was set as shown in Figure 4. For an efficient mesh generation, calculation domain
was divided into a cylindrical inner part surrounding the ship and a cubic outer. These two domains
were filled with tetrahedral meshes. Total number of the meshes is about 500,000.
332x58~63
Figure 4: Calculation Domain
3.2.2 Calculation setting
The ship is advancing with its speed in a wind. And nitrogen dioxide is included in the exhaust gas
with the concentration of 1200 ppm. Although many other noxious gases are included in real exhausts,
they need not be included in the analysis because their concentrations are generally too low to cause
on-board pollution.
Principal features of the analysis are summarized in TABLE 2. Multiple species model was adopted in
order to simulate the dispersion of nitrogen dioxide and energy equation was included into the
governing equation set because of the high temperature at the exits of the exhausts.
TABLE 1
PRINCIPAL FEATURES OF THE ANALYSIS
Coordinate system ' Right-handed Cartesian coordinate system, vertically upward z-axis
Problem type 3D steady state, energy equation included
Solver Segregated explicit
Turbulence model RNG k-E model with standard wall function
Discretization Standard for Dressure. fist order uDwind for all the other variables
3.3 Evaluation of the Smoke Exhaust Performance
Some measures are required to judge the smoke exhaust performance from simulation results. Those
can be prepared considering the problems caused by exhaust gas from the funnel exhausts. For a
common merchant ship, the problems caused by exhaust gas can be divided into two categories. The
first is the dispersion of the noxious gases, and the second is the possibility of pollution caused by ash
included in the exhaust. In this study, following items are introduced for the purpose of the evaluation
of the smoke exhaust performance:
3.3. I Dispersion of the noxious gas
As mentioned before, nitrogen dioxide was adopted as a typical noxious gas. It starts with
concentration of 1200 ppm and disperses rapidly. If its concentration at the deckhouse, engine room
intake or other principal points is higher than a certain value, there exists a possibility of health
problem of the crews. Two methods were adopted to inspect the dispersion of nitrogen dioxide. The
first is to observe the shape of the iso-surface of NO2 concentration. The region covered with the iso-