Page 189 - Practical Power System and Protective Relays Commissioning
P. 189
Protection Relays Chapter | 18 191
18.3.1 DESIGN CRITERIA OF PROTECTIVE RELAYING
SYSTEMS
1. Reliability
The ability of the protective system to perform correctly when needed
(dependability) and to avoid unnecessary operation (security).
2. Speed
This is the operating time of the relay, which is a very important
factor to reduce the fault damage effects on the system.
3. Selectivity
This is the maximum service continuity with minimum system
disconnection and is done by tripping the only faulted part of the system
and leaving the healthy part of the system in operation (refer to
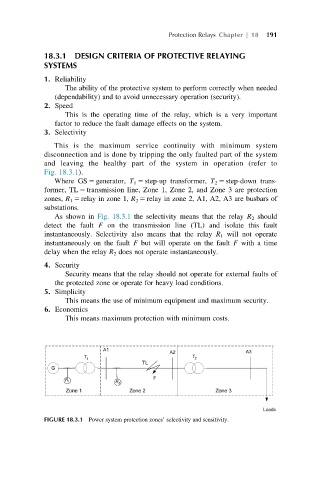
Fig. 18.3.1).
Where GS 5 generator, T 1 5 step-up transformer, T 2 5 step-down trans-
former, TL 5 transmission line, Zone 1, Zone 2, and Zone 3 are protection
zones, R 1 5 relay in zone 1, R 2 5 relay in zone 2, A1, A2, A3 are busbars of
substations.
As shown in Fig. 18.3.1 the selectivity means that the relay R 2 should
detect the fault F on the transmission line (TL) and isolate this fault
instantaneously. Selectivity also means that the relay R 1 will not operate
instantaneously on the fault F but will operate on the fault F with a time
delay when the relay R 2 does not operate instantaneously.
4. Security
Security means that the relay should not operate for external faults of
the protected zone or operate for heavy load conditions.
5. Simplicity
This means the use of minimum equipment and maximum security.
6. Economics
This means maximum protection with minimum costs.
FIGURE 18.3.1 Power system protection zones’ selectivity and sensitivity.