Page 462 - Practical Well Planning and Drilling Manual
P. 462
Appendix NEW! revised 11/00/bc 1/30/01 3:29 PM Page 438
[ ]
Appendix 1
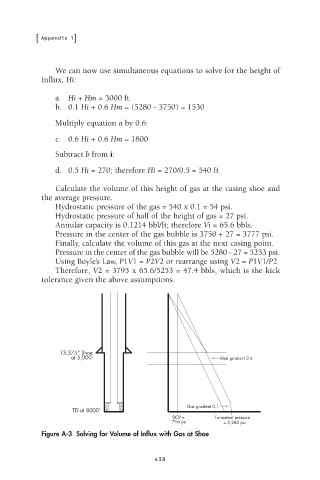
We can now use simultaneous equations to solve for the height of
influx, Hi:
a. Hi + Hm = 3000 ft
b. 0.1 Hi + 0.6 Hm = (5280 - 3750) = 1530
Multiply equation a by 0.6:
c. 0.6 Hi + 0.6 Hm = 1800
Subtract b from i:
d. 0.5 Hi = 270; therefore Hi = 270/0.5 = 540 ft
Calculate the volume of this height of gas at the casing shoe and
the average pressure.
Hydrostatic pressure of the gas = 540 x 0.1 = 54 psi.
Hydrostatic pressure of half of the height of gas = 27 psi.
Annular capacity is 0.1214 bbl/ft; therefore Vi = 65.6 bbls.
Pressure in the center of the gas bubble is 3750 + 27 = 3777 psi.
Finally, calculate the volume of this gas at the next casing point.
Pressure in the center of the gas bubble will be 5280 - 27 = 5253 psi.
Using Boyle’s Law, P1V1 = P2V2 or rearrange using V2 = P1V1/P2
Therefore, V2 = 3795 x 65.6/5253 = 47.4 bbls, which is the kick
tolerance given the above assumptions.
13.375" Shoe
at 5,000' Mud gradient 0.6
Gas gradient 0.1
TD at 8000'
SICP = Formation pressure
716 psi = 5,280 psi
Figure A-3 Solving for Volume of Influx with Gas at Shoe
438