Page 234 - Pressure Vessel Design Manual
P. 234
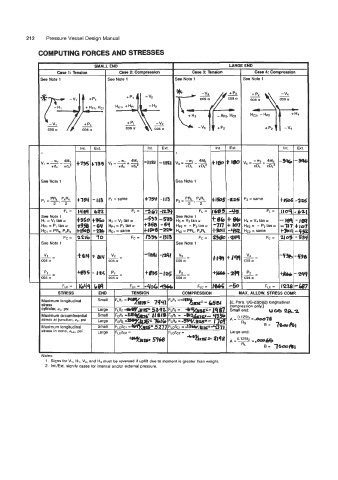
212 Pressure Vessel Design Manual
COMPUTING FORCES AND STRESSES
SMALL END LARGE END
Case 1: Rnsion Case 2 Compression Case 3 Tenslon Case 4 Cornwemion
be Note I he Note 1 See Note 1 See Note 1
Hci. +:f;v2
- -
COS a COS a
Int. I ~xt. int. Ext.
- IRI -996 -si
see Note 1 See Note 1
D1 = same - 10 P2 = same f-#e5 -2a
FL = FL = FL = FL = rroq -61.
see Note 1 See Note 1
i1 = v1 tan a H2 = Vp tan a H3 = V3 tan a H4 = V4 tan a -le9 -1%
ipl = P1 tan a Hpl = Pt tan a Hm= - P2tana Hm= -PZtana -717 t 10:
icl = PRs, PxRs Hcl = same He - PRL, P~RL HCP = same t3mr -4s
Fc = Fc = Fc = Fc = a05 - 53'
See Note 1 See Note 1
vi -IW -&t
v3 -
v4
-= -- -= -4% - 43c
DS a COS a COS a
I
p1= -= +893 -125 pP= -= +## -24
P2
Pl
DS a :os a cos a COS a
FLC = FLC = FLC = 12% -cB;
~
STRESS COMPRESSION I MAX. ALLOW. STRESS COMP.
daximurn longitudinal
stress
cylinder. UL, psi
Maximum circumferential
stress at junction, u,, psi
Maximum longitudinal
stress in cone, uLC, psi
Notes:
1. Signs for Vl, HI, VI. and H3 must be reversed if uplift due to moment is greater than weight.
2. Int.lExt. signify cases for internal andlor external pressure.