Page 192 - Primer on Enhanced Oil Recovery
P. 192
182 Primer on Enhanced Oil Recovery
The static model includes the geological model of the field. The geological
model is a framework of a field divided into millions of cells, where each cell con-
tains all the petrophysical and reservoir-filtration parameters of a given field.
A dynamic model is a hydrodynamic model of a field. Data on a three-
dimensional geological model, perforation, production, formation effects and other
dynamic data are loaded into the hydrodynamic model. This allows for detailed
forecasting based on the field development history.
15.1 Geological modeling
Currently, the main software packages for creating 3D geological models of oil and
gas fields are: DecisionSpase and Geographix (Landmark); IRAPRMS (Roxar);
Petrel (Schlumberger); Gocad (Paradigm) and few others.
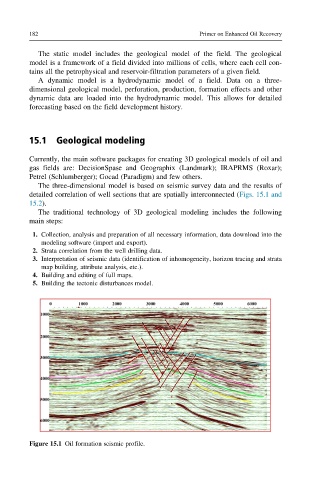
The three-dimensional model is based on seismic survey data and the results of
detailed correlation of well sections that are spatially interconnected (Figs. 15.1 and
15.2).
The traditional technology of 3D geological modeling includes the following
main steps:
1. Collection, analysis and preparation of all necessary information, data download into the
modeling software (import and export).
2. Strata correlation from the well drilling data.
3. Interpretation of seismic data (identification of inhomogeneity, horizon tracing and strata
map building, attribute analysis, etc.).
4. Building and editing of full maps.
5. Building the tectonic disturbances model.
Figure 15.1 Oil formation seismic profile.