Page 198 - Primer on Enhanced Oil Recovery
P. 198
EOR modeling 187
Further, on the basis of the constructed geological model, a hydrodynamic model
of the field is created, which allows flexible management and the development of
an optimal oil field development strategy.
However, the main problem in the preparation of oil exploiration project plans
arises due to discrepancies between the static (geological) and filtration (hydrody-
namic) models. It is clear that the models cannot produce absolutely identical
results, newetheless, it is widely accepted, that the static and filtration models
should differ from each other by no more than 3%.
15.2 Hydrodynamic modeling
The main software packages for creating hydrodynamic models of oil and gas
fields are VIP and Nexus (Landmark), Tempest More (Roxar) and Eclipse
(Schlumberger).
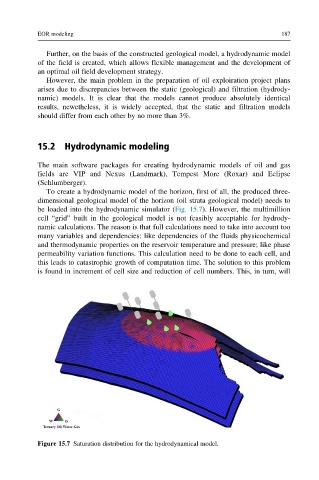
To create a hydrodynamic model of the horizon, first of all, the produced three-
dimensional geological model of the horizon (oil strata geological model) needs to
be loaded into the hydrodynamic simulator (Fig. 15.7). However, the multimillion
cell “grid” built in the geological model is not feasibly acceptable for hydrody-
namic calculations. The reason is that full calculations need to take into account too
many variables and dependencies: like dependencies of the fluids physicochemical
and thermodynamic properties on the reservoir temperature and pressure; like phase
permeability variation functions. This calculation need to be done to each cell, and
this leads to catastrophic growth of computation time. The solution to this problem
is found in increment of cell size and reduction of cell numbers. This, in turn, will
Figure 15.7 Saturation distribution for the hydrodynamical model.