Page 204 - Primer on Enhanced Oil Recovery
P. 204
Reservoir characteristics
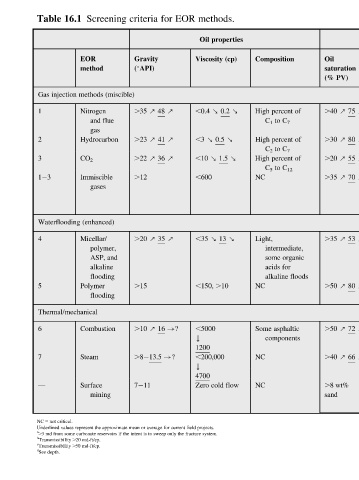
saturation Temperature Depth (ft) Average Net thickness Formation type ( F) permeability (ft) (md) (% PV) NC .6000 NC Thin unless Sandstone or .40 s 75 s dipping carbonate NC .4000 NC Thin unless Sandstone or .30 s 80 s dipping carbonate NC .2500 NC Wide range Sandstone or .20 s 55 s carbonate NC .1800 NC NC
Oil sand
Composition High percent of C 1 to C 7 High percent of C 2 to C 7 High percent of C 5 to C 12 NC Light, intermediate, some organic acids for alkaline floods NC Some asphaltic components NC NC
methods. Oil properties Viscosity (cp) ,0.4 r 0.2 r ,3 r 0.5 r ,10 r 1.5 r ,600 ,35 r 13 r ,150, .10 ,5000 1200 ,200,000 4700 Zero cold flow
EOR k k
for .10 s 16 !?
criteria Gravity ( API) .35 s 48 s .23 s 41 s .22 s 36 s .12 .20 s 35 s .15 .8 13.5 !? 7 11 Underlined values represent the approximate mean or average for current field projects. a .3 md from some carbonate reservoirs if the intent is to sweep only the fracture system.
Screening method Nitrogen and flue gas Hydrocarbon Immiscible gases Micellar/ polymer, ASP, and alkaline flooding Polymer flooding Combustion Surface mining
16.1 EOR Gas injection methods (miscible) CO 2 Waterflooding (enhanced) Thermal/mechanical Steam b Transmissibility .20 md-ft/cp. c Transmissibility .50 md-ft/cp.
Table 1 2 3 1 3 4 5 6 7 — NC 5 not critical. d See depth.