Page 81 - Primer on Enhanced Oil Recovery
P. 81
72 Primer on Enhanced Oil Recovery
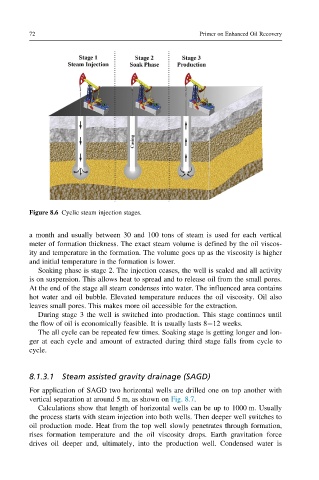
Figure 8.6 Cyclic steam injection stages.
a month and usually between 30 and 100 tons of steam is used for each vertical
meter of formation thickness. The exact steam volume is defined by the oil viscos-
ity and temperature in the formation. The volume goes up as the viscosity is higher
and initial temperature in the formation is lower.
Soaking phase is stage 2. The injection ceases, the well is sealed and all activity
is on suspension. This allows heat to spread and to release oil from the small pores.
At the end of the stage all steam condenses into water. The influenced area contains
hot water and oil bubble. Elevated temperature reduces the oil viscosity. Oil also
leaves small pores. This makes more oil accessible for the extraction.
During stage 3 the well is switched into production. This stage continues until
the flow of oil is economically feasible. It is usually lasts 8 12 weeks.
The all cycle can be repeated few times. Soaking stage is getting longer and lon-
ger at each cycle and amount of extracted during third stage falls from cycle to
cycle.
8.1.3.1 Steam assisted gravity drainage (SAGD)
For application of SAGD two horizontal wells are drilled one on top another with
vertical separation at around 5 m, as shown on Fig. 8.7.
Calculations show that length of horizontal wells can be up to 1000 m. Usually
the process starts with steam injection into both wells. Then deeper well switches to
oil production mode. Heat from the top well slowly penetrates through formation,
rises formation temperature and the oil viscosity drops. Earth gravitation force
drives oil deeper and, ultimately, into the production well. Condensed water is