Page 139 - Principles of Applied Reservoir Simulation 2E
P. 139
124 Principles of Applied Reservoir Simulation
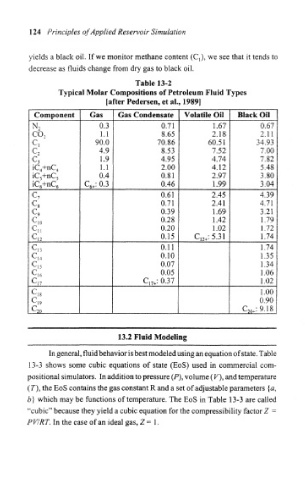
yields a black oil. If we monitor methane content (C,), we see that it tends to
decrease as fluids change from dry gas to black oil.
Table 13-2
Typical Molar Compositions of Petroleum Fluid Types
[after Pedersen, et al., 1989]
Component Gas Gas Condensate Volatile Oil Black Oil
0.3 0.71 1.67 0.67
N 2
1.1 8.65 2.18 2.11
C0 2
C, 90.0 70.86 60.51 34.93
4.9 8.53 7.52 7.00
C 2
€3 1.9 4.95 4.74 7.82
1.1 2.00 4.12 5.48
iC 4+nC 4
0.4 0.81 2.97 3.80
iC 5+nC 5
C 6+: 0.3 0.46 1.99 3.04
iC 6+nC 6
0.61 2.45 4.39
C 7
0.71 2.41 4.71
C 8
0.39 1.69 3.21
C 9
0.28 1.42 1,79
C 10
c,, 0.20 1.02 1.72
0.15 C !2+:5.31 1.74
C 12
0.11 1.74
C 13
0.10 1.35
C 14 0.07 1,34
C ss
c,; 0.05 1.06
CP C 17+: 0.37 1.02
v-qg 1.00
0.90
1 9
C 20.:9.18
^20
13.2 Fluid Modeling
In general, fluid behavior is best modeled using an equation of state. Table
13-3 shows some cubic equations of state (EoS) used in commercial com-
positional simulators. In addition to pressure (P), volume (V), and temperature
(T), the EoS contains the gas constant R and a set of adjustable parameters (a,
b} which may be functions of temperature. The EoS in Table 13-3 are called
"cubic" because they yield a cubic equation for the compressibility factor Z =
PVIRT. In the case of an ideal gas, Z - 1.