Page 148 - Principles of Applied Reservoir Simulation 2E
P. 148
Part II: Reservoir Simulation 133
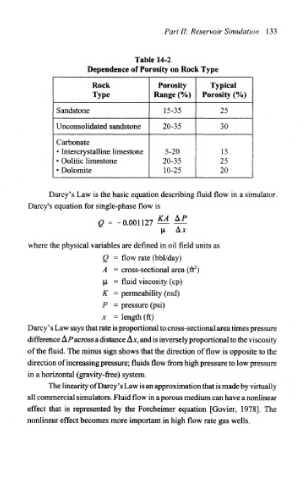
Table 14-2
Dependence of Porosity on Rock Type
Rock Porosity Typical
Type Range (%) Porosity (%)
Sandstone 15-35 25
Unconsolidated sandstone 20-35 30
Carbonate
« Intercrystalline limestone 5-20 15
• Oolitic limestone 20-35 25
• Dolomite 10-25 20
Darcy's Law is the basic equation describing fluid flow in a simulator.
Darcy's equation for single-phase flow is
Q = -0.001127
Ax
where the physical variables are defined in oil field units as
Q = flow rate (bbl/day)
2
A = cross-sectional area (ft )
|l = fluid viscosity (cp)
K = permeability (md)
P = pressure (psi)
x = length (ft)
Darcy's Law says that rate is proportional to cross-sectional area times pressure
difference AP across a distance A jc, and is inversely proportional to the viscosity
of the fluid. The minus sign shows that the direction of flow is opposite to the
direction of increasing pressure; fluids flow from high pressure to low pressure
in a horizontal (gravity-free) system.
The linearity of Darcy's Law is an approximation that is made by virtually
all commercial simulators. Fluid flow in a porous medium can have a nonlinear
effect that is represented by the Forcheimer equation [Govier, 1978]. The
nonlinear effect becomes more important in high flow rate gas wells.