Page 16 - Principles of Catalyst Development
P. 16
2 CHAPTER I
50 - rate catalytic
= 3 x 10 13
rate homogeneous
40
30 o
E
~
.. 20 W c
w
...J r- o
0
~ 10
...J
<t
U
:.:: 0
)--
l!)
a:: -10
w
z
w
-20
-30 l
I
REACTION -
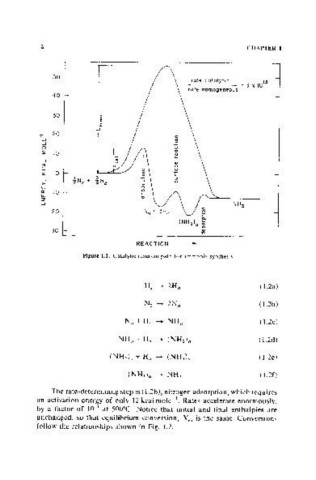
Figure 1.1. Catalytic reaction path for ammonia synthesis.
H2 -+ 2Ha ( 1.2a)
N2 -+ 2Na (1.2b)
N" + Ha -+ NHa (I .2c)
NHa + Ha -+ (NH 2)a ( 1.2d)
(NH 2 )a + Ha -+ (NH 3 )a (l.2e)
(NH]L -+ NH J ( 1.2f)
The rate-determining step is (1.2b), nitrogen adsorption, which requires
an activation energy of only 12 kcal mole-I. Rates accelerate enormously,
by a factor of IOiJ at 50()°C. Notice that initial and final enthalpies are
unchanged, so that equilibrium conversion, X" is the same. Conversions
follow the relationships shown in Fig. 1.2.