Page 127 - Probability Demystified
P. 127
116 CHAPTER 7 The Binomial Distribution
The outcomes can be arranged according to the number of heads, as
shown.
0 heads TTT
1 head TTH, THT, HTT
2 heads THH, HTH, HHT
3 heads HHH
Finally, the outcomes and corresponding probabilities can be written in a
table, as shown.
Outcome, x 0 1 2 3
1 3 3 1
Probability, P(x)
8 8 8 8
The sum of the probabilities of a probability distribution must be 1.
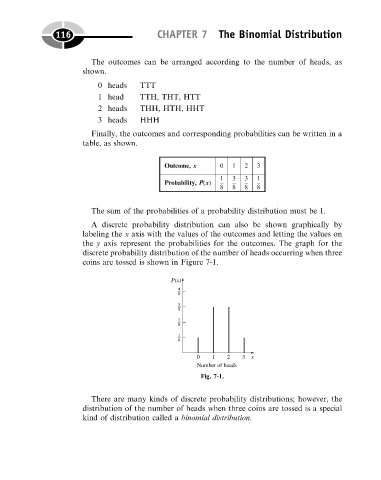
A discrete probability distribution can also be shown graphically by
labeling the x axis with the values of the outcomes and letting the values on
the y axis represent the probabilities for the outcomes. The graph for the
discrete probability distribution of the number of heads occurring when three
coins are tossed is shown in Figure 7-1.
Fig. 7-1.
There are many kinds of discrete probability distributions; however, the
distribution of the number of heads when three coins are tossed is a special
kind of distribution called a binomial distribution.