Page 537 - Probability and Statistical Inference
P. 537
514 11. Likehood Ratio and Other Tests
its behavior to check when it is small (< k). We note that g(1) = 1 and g (u) =
{(1 - u)/u}g(u) which is positive (negative) when u < 1 (u > 1). Hence, the
function g(u) is strictly increasing (decreasing) on the left (right) hand side of
u = 1. Thus, g(u) is going to be small for both very small and very large
values of u(> 0). This feature is also clear from the plot of the function g(u)
given in the Figure 11.2.1. Thus, we rewrite the LR test (11.2.19) as follows:
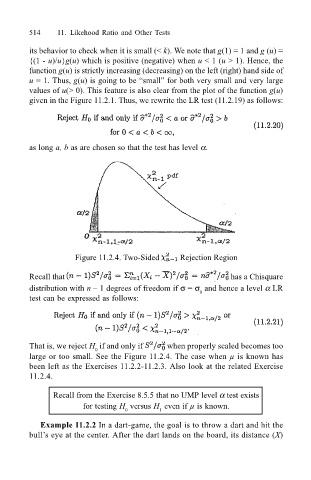
as long a, b as are chosen so that the test has level α.
Figure 11.2.4. Two-Sided Rejection Region
Recall that has a Chisquare
distribution with n 1 degrees of freedom if σ = σ and hence a level α LR
0
test can be expressed as follows:
That is, we reject H if and only if when properly scaled becomes too
0
large or too small. See the Figure 11.2.4. The case when µ is known has
been left as the Exercises 11.2.2-11.2.3. Also look at the related Exercise
11.2.4.
Recall from the Exercise 8.5.5 that no UMP level α test exists
for testing H versus H even if µ is known.
0 1
Example 11.2.2 In a dart-game, the goal is to throw a dart and hit the
bulls eye at the center. After the dart lands on the board, its distance (X)