Page 533 - Probability and Statistical Inference
P. 533
510 11. Likehood Ratio and Other Tests
may be small or large at the same time. Thus, more formally, one
rejects H if and only if Λ is small. Thus, we decide as follows:
0
where k(> 0) is a generic constant. That is, we reject H if and only if
0
is too large (> ) or too small (< ). The implementable form of the level
α LR test will look like this:
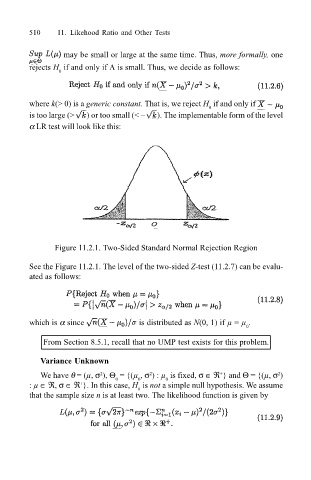
Figure 11.2.1. Two-Sided Standard Normal Rejection Region
See the Figure 11.2.1. The level of the two-sided Z-test (11.2.7) can be evalu-
ated as follows:
which is α since is distributed as N(0, 1) if µ = µ .
0
From Section 8.5.1, recall that no UMP test exists for this problem.
Variance Unknown
2
2
+
2
We have θ = (µ, σ ), Θ = {(µ , σ ) : µ is fixed, σ ∈ ℜ } and Θ = {(µ, σ )
0
0
0
: µ ∈ ℜ, σ ∈ ℜ }. In this case, H is not a simple null hypothesis. We assume
+
0
that the sample size n is at least two. The likelihood function is given by