Page 653 - Probability and Statistical Inference
P. 653
630 14. Appendix
14.3.4 Percentage Points of the F Distribution
The Table 14.3.4 provides the lower 100γ% point F ν1, ν2, 1-γ for the F ν1, ν2 distri-
bution for different values of ν , ν and γ. See the Figure 14.3.5.
1 2
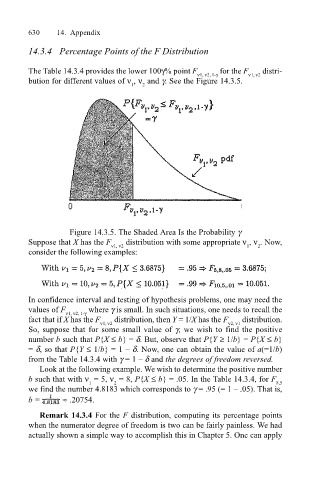
Figure 14.3.5. The Shaded Area Is the Probability γ
Suppose that X has the F ν1, ν2 distribution with some appropriate ν , ν . Now,
2
1
consider the following examples:
In confidence interval and testing of hypothesis problems, one may need the
values of F ν1, ν2, 1-γ where γ is small. In such situations, one needs to recall the
fact that if X has the F ν1, ν2 distribution, then Y = 1/X has the F ν2, ν1 distribution.
So, suppose that for some small value of γ, we wish to find the positive
number b such that P{X ≤ b} = δ. But, observe that P{Y ≥ 1/b} = P{X ≤ b}
= δ, so that P{Y ≤ 1/b} = 1 δ. Now, one can obtain the value of a(=1/b)
from the Table 14.3.4 with γ = 1 δ and the degrees of freedom reversed.
Look at the following example. We wish to determine the positive number
b such that with ν = 5, ν = 8, P{X ≤ b} = .05. In the Table 14.3.4, for F 8,5
2
1
we find the number 4.8183 which corresponds to γ = .95 (= 1 .05). That is,
b = ≈ .20754.
Remark 14.3.4 For the F distribution, computing its percentage points
when the numerator degree of freedom is two can be fairly painless. We had
actually shown a simple way to accomplish this in Chapter 5. One can apply