Page 188 - Process Equipment and Plant Design Principles and Practices by Subhabrata Ray Gargi Das
P. 188
186 Chapter 6 Evaporators
Vapour
V
h V
T
P P
T = Ts (P)
+BPE (x)
Steam
S
h Steam
Thick liquor
T Steam L
P Steam x
Feed h L
F T
x F
h F
T F Condensate
S
h con
T con = T (P Steam )
s
P Steam
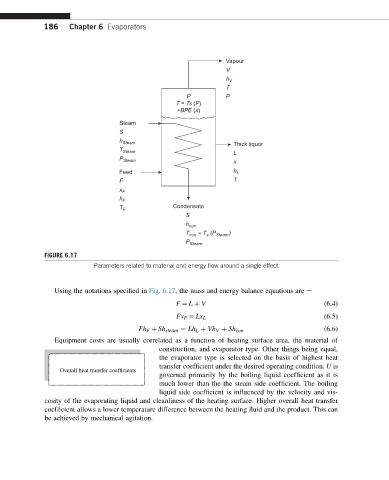
FIGURE 6.17
Parameters related to material and energy flow around a single effect.
Using the notations specified in Fig. 6.17, the mass and energy balance equations are e
F ¼ L þ V (6.4)
(6.5)
Fx F ¼ Lx L
Fh F þ Sh steam ¼ Lh L þ Vh V þ Sh con (6.6)
Equipment costs are usually correlated as a function of heating surface area, the material of
construction, and evaporator type. Other things being equal,
the evaporator type is selected on the basis of highest heat
transfer coefficient under the desired operating condition. U is
Overall heat transfer coefficients
governed primarily by the boiling liquid coefficient as it is
much lower than the the steam side coefficient. The boiling
liquid side coefficient is influenced by the velocity and vis-
cosity of the evaporating liquid and cleanliness of the heating surface. Higher overall heat transfer
coefficient allows a lower temperature difference between the heating fluid and the product. This can
be achieved by mechanical agitation.