Page 202 - Process Equipment and Plant Design Principles and Practices by Subhabrata Ray Gargi Das
P. 202
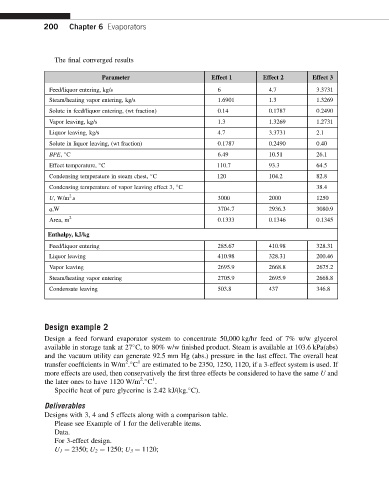
200 Chapter 6 Evaporators
The final converged results
Parameter Effect 1 Effect 2 Effect 3
Feed/liquor entering, kg/s 6 4.7 3.3731
Steam/heating vapor entering, kg/s 1.6901 1.3 1.3269
Solute in feed/liquor entering, (wt fraction) 0.14 0.1787 0.2490
Vapor leaving, kg/s 1.3 1.3269 1.2731
Liquor leaving, kg/s 4.7 3.3731 2.1
Solute in liquor leaving, (wt fraction) 0.1787 0.2490 0.40
BPE, C 6.49 10.51 26.1
Effect temperature, C 110.7 93.3 64.5
Condensing temperature in steam chest, C 120 104.2 82.8
Condensing temperature of vapor leaving effect 3, C 38.4
2
U, W/m .s 3000 2000 1250
q,W 3704.7 2936.3 3080.9
Area, m 2 0.1333 0.1346 0.1345
Enthalpy, kJ/kg
Feed/liquor entering 285.67 410.98 328.31
Liquor leaving 410.98 328.31 200.46
Vapor leaving 2695.9 2668.8 2675.2
Steam/heating vapor entering 2705.9 2695.9 2668.8
Condensate leaving 503.8 437 346.8
Design example 2
Design a feed forward evaporator system to concentrate 50,000 kg/hr feed of 7% w/w glycerol
available in storage tank at 27 C, to 80% w/w finished product. Steam is available at 103.6 kPa(abs)
and the vacuum utility can generate 92.5 mm Hg (abs.) pressure in the last effect. The overall heat
1
transfer coefficients in W/m . C are estimated to be 2350, 1250, 1120, if a 3-effect system is used. If
2
more effects are used, then conservatively the first three effects be considered to have the same U and
1
the later ones to have 1120 W/m . C .
2
Specific heat of pure glycerine is 2.42 kJ/(kg. C).
Deliverables
Designs with 3, 4 and 5 effects along with a comparison table.
Please see Example of 1 for the deliverable items.
Data.
For 3-effect design.
U 1 ¼ 2350; U 2 ¼ 1250; U 3 ¼ 1120;