Page 320 - Process Equipment and Plant Design Principles and Practices by Subhabrata Ray Gargi Das
P. 320
322 Chapter 11 Distillation
11.6.2 Design considerations
The following considerations are helpful in proceeding with the design
• Lower operating pressures require lower drum temperature and lower heating load.
• Pressure versus vacuum operation e A slight positive pressure is usually preferred in case of
combustible systems in order to avoid/reduce the risk of air ingress into the drum. Air ingress may
lead to an explosive mixture and is particularly important while handling hydrocarbons. Vacuum
flashing is resorted to when there is a maximum limit of a lighter component concentration in the
liquid or when maximum recovery of a lighter component is warranted. Operating under vacuum
requires a lower operating temperature and heat load but increases vapour volume which in turn
results in larger drum size. Vacuum in most cases is created by a steam ejector. Ejector steam
consumption increases sharply with higher vacuum requirement and the steam cost may offset the
other advantages of vacuum operation. Unless there is some specific requirement, the operating
pressure lower limit is kept w0.1 atm (abs). This level of vacuum is easily achieved by a steam
ejector coupled with a barometric condenser.
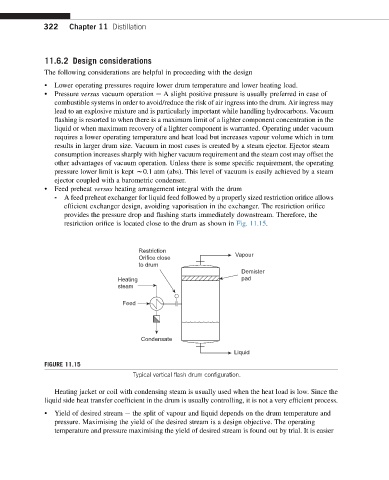
• Feed preheat versus heating arrangement integral with the drum
- A feed preheat exchanger for liquid feed followed by a properly sized restriction orifice allows
efficient exchanger design, avoiding vaporisation in the exchanger. The restriction orifice
provides the pressure drop and flashing starts immediately downstream. Therefore, the
restriction orifice is located close to the drum as shown in Fig. 11.15.
Restriction
Vapour
Orifice close
to drum
Demister
Heating pad
steam
Feed
Condensate
Liquid
FIGURE 11.15
Typical vertical flash drum configuration.
Heating jacket or coil with condensing steam is usually used when the heat load is low. Since the
liquid side heat transfer coefficient in the drum is usually controlling, it is not a very efficient process.
• Yield of desired stream e the split of vapour and liquid depends on the drum temperature and
pressure. Maximising the yield of the desired stream is a design objective. The operating
temperature and pressure maximising the yield of desired stream is found out by trial. It is easier